The space left in the chest allows the lungs to expand. They keep subdividing and branching, ending in terminal and lastly in respiratory bronchioles which bring the air into alveoli. During breathing, it is the chief muscle of inspiration. The oxygen then moves into an erythrocyte and binds to a molecule of hemoglobin.  By adolescence, the normal respiratory rate is similar to that of adults, 12 to 18 breaths per minute. The following sections will look at some respiratory conditions in more detail. There are two phases of breathing: in and out. The respiratory system helps prevent the intake of harmful particles such as dust, fumes, and mist through coughing, sneezing, or swallowing. The normal respiratory rate of a child decreases from birth to adolescence. Basically, the affected portion of the wall moves inwards on inspiration and outwards on expiration (paradoxical motion), creating pain and impairing ventilation. Breathing is one of the four components of respiration, the other three being gas diffusion, gas transport and regulation. The VRG is involved in maintaining a constant breathing rhythm by stimulating the diaphragm and intercostal muscles to contract, resulting in inspiration. During a breathing cycle, the lungs can be expanded and contracted in two ways. The lungs themselves are passive during breathing, meaning they are not involved in creating the movement that helps inspiration and expiration. The information we provide is grounded on academic literature and peer-reviewed research. (3) Air moves into the nose and down the trache . According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), around 7.7% of adults in the United States have asthma. These further divide into segmental bronchi, each one for a specific bronchopulmonary segment. Wise, Eddie Johnson, Brandon Poe, Dean H. Kruse, Oksana Korol, Jody E. Johnson, Mark Womble, Peter DeSaix. Creative Commons Attribution License The upper tract comprises: The sections below will look at each part of the respiratory system in more detail. The dome shaped thoracic cage provides the necessary rigidity for organ protection, weight support for the upper limbs and anchorage for muscles. They form most of the thoracic cage, extending from the posterior to the anterior thoracic walls. The normal respiratory rate of a child decreases from birth to adolescence. Inhalation and Exhalation: In breathing, we take in oxygen and give out carbon In order for air to be drawn into the lungs during inhalation Can diet help improve depression symptoms? When the diaphragm contracts, it moves inferiorly toward the abdominal cavity, creating a larger thoracic cavity and more space for the lungs. However, some medical conditions, such as stroke and congestive heart failure, may cause damage to the pons or medulla oblongata. By fixing the scapula in position, this muscle has an important role in laboured breathing when grasping a support or staying in the so-called tripod position. The conducting airways consist of the following: In addition to carrying the air, they also filter, humidify and warm it. Since the parietal pleura is attached to the thoracic wall, the natural elasticity of the chest wall opposes the inward pull of the lungs. The dorsal respiratory group within the dorsal portion of the medulla is responsible for the largest part of the breathing cycle. Pressure and volume are inversely related (P = k/V). It is a dose-response, negative-feedback relationship in which the greater the stimulus, the greater the response. Write a flowchart explaining the process of respiration Get the answers you need, now! All rights reserved. A higher transpulmonary pressure corresponds to a larger lung. These actions increase the volume of the thoracic (chest) cavity, and the air (oxygen) is forced into the lungs. Removal of carbon dioxide from the blood helps to reduce hydrogen ions, thus increasing systemic pH. The Reading time: 20 minutes. Contraction and relaxation of the diaphragm and intercostals muscles (found between the ribs) cause most of the pressure changes that result in inspiration and expiration. Air flows out of the lungs during expiration based on the same principle; when the lungs recoil, pressure within the lungs becomes greater than the atmospheric pressure. Concentrations of chemicals are sensed by chemoreceptors. In the medical world, breathing is defined as pulmonary ventilation, described as the movement of air between the atmosphere and the lung alveoli . Ultimately, the outward pull is slightly greater than the inward pull, creating the 4 mm Hg intrapleural pressure relative to the intra-alveolar pressure. In some cases, the cause of central sleep apnea is unknown. Alveolar dead space involves air found within alveoli that are unable to function, such as those affected by disease or abnormal blood flow. When you inhale, you breath in oxygen which travels through the lungs to the alveoli/capillary for gas exchange. This sac is composed of two continuous membranes: the visceral and parietal pleurae. Except where otherwise noted, textbooks on this site TLC is about 6000 mL air for males, and about 4200 mL for females. One way of doing this is to change the anteroposterior diameter of the chest cavity by elevating or depressing the ribs. Some carbon dioxide travels in erythrocytes, but most of it travels in the plasma and may be in the form of carbonic acid (a weak acid) or sodium bicarbonate (a weak base) to help balance the pH of the blood. The larynx has a dual function in the respiratory system: as an air canal to the lungs (while stopping food and drink from blocking the airway) and as the voice box (which contains vocal cords for speech). They are attached at their anterior ends by costal cartilages, which either provide direct attachment to the sternum , or the costal margin. The potential for movement is related to the flexibility provided by the ribs and their joints. The diaphragm operates as the major muscle of respiration and aids breathing. It involves two events: inspiration, when the air moves into the lungsand expiration, when the air leaves the lungs. In contrast, low levels of carbon dioxide in the blood cause low levels of hydrogen ions in the brain, leading to a decrease in the rate and depth of pulmonary ventilation, producing shallow, slow breathing. Boyles law is expressed by the following formula: In this formula, P1 represents the initial pressure and V1 represents the initial volume, whereas the final pressure and volume are represented by P2 and V2, respectively. Pulmonary ventilation is the act of breathing, which can be described as the movement of air into and out of the lungs. They consist of scalenus anterior, scalenus medius and scalenus posterior. WebControl of. The trachea is a tube-like passage that runs down the neck and upper chest, carrying air to and from the lungs. Symptoms include a high temperature, a cough, difficulty breathing, and chest pain. Therefore, the pressure is lower in the two-liter container and higher in the one-liter container. The base is the concave inferior surface that rests directly on the diaphragm. In this case, the force exerted by the movement of the gas molecules against the walls of the two-liter container is lower than the force exerted by the gas molecules in the one-liter container. We avoid using tertiary references. Lung anatomy can get quite complicated extremely quickly. Oxygen enters the lungs, then the bloodstream, allowing the body to function normally. By the end of this section, you will be able to: Pulmonary ventilation is the act of breathing, which can be described as the movement of air into and out of the lungs. Resistance is a force that slows motion, in this case, the flow of gases. Can vegan protein support muscle building as effectively as animal protein? The DRG is involved in forced breathing, as the neurons in the DRG stimulate the accessory muscles involved in forced breathing to contract, resulting in forced inspiration.
By adolescence, the normal respiratory rate is similar to that of adults, 12 to 18 breaths per minute. The following sections will look at some respiratory conditions in more detail. There are two phases of breathing: in and out. The respiratory system helps prevent the intake of harmful particles such as dust, fumes, and mist through coughing, sneezing, or swallowing. The normal respiratory rate of a child decreases from birth to adolescence. Basically, the affected portion of the wall moves inwards on inspiration and outwards on expiration (paradoxical motion), creating pain and impairing ventilation. Breathing is one of the four components of respiration, the other three being gas diffusion, gas transport and regulation. The VRG is involved in maintaining a constant breathing rhythm by stimulating the diaphragm and intercostal muscles to contract, resulting in inspiration. During a breathing cycle, the lungs can be expanded and contracted in two ways. The lungs themselves are passive during breathing, meaning they are not involved in creating the movement that helps inspiration and expiration. The information we provide is grounded on academic literature and peer-reviewed research. (3) Air moves into the nose and down the trache . According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), around 7.7% of adults in the United States have asthma. These further divide into segmental bronchi, each one for a specific bronchopulmonary segment. Wise, Eddie Johnson, Brandon Poe, Dean H. Kruse, Oksana Korol, Jody E. Johnson, Mark Womble, Peter DeSaix. Creative Commons Attribution License The upper tract comprises: The sections below will look at each part of the respiratory system in more detail. The dome shaped thoracic cage provides the necessary rigidity for organ protection, weight support for the upper limbs and anchorage for muscles. They form most of the thoracic cage, extending from the posterior to the anterior thoracic walls. The normal respiratory rate of a child decreases from birth to adolescence. Inhalation and Exhalation: In breathing, we take in oxygen and give out carbon In order for air to be drawn into the lungs during inhalation Can diet help improve depression symptoms? When the diaphragm contracts, it moves inferiorly toward the abdominal cavity, creating a larger thoracic cavity and more space for the lungs. However, some medical conditions, such as stroke and congestive heart failure, may cause damage to the pons or medulla oblongata. By fixing the scapula in position, this muscle has an important role in laboured breathing when grasping a support or staying in the so-called tripod position. The conducting airways consist of the following: In addition to carrying the air, they also filter, humidify and warm it. Since the parietal pleura is attached to the thoracic wall, the natural elasticity of the chest wall opposes the inward pull of the lungs. The dorsal respiratory group within the dorsal portion of the medulla is responsible for the largest part of the breathing cycle. Pressure and volume are inversely related (P = k/V). It is a dose-response, negative-feedback relationship in which the greater the stimulus, the greater the response. Write a flowchart explaining the process of respiration Get the answers you need, now! All rights reserved. A higher transpulmonary pressure corresponds to a larger lung. These actions increase the volume of the thoracic (chest) cavity, and the air (oxygen) is forced into the lungs. Removal of carbon dioxide from the blood helps to reduce hydrogen ions, thus increasing systemic pH. The Reading time: 20 minutes. Contraction and relaxation of the diaphragm and intercostals muscles (found between the ribs) cause most of the pressure changes that result in inspiration and expiration. Air flows out of the lungs during expiration based on the same principle; when the lungs recoil, pressure within the lungs becomes greater than the atmospheric pressure. Concentrations of chemicals are sensed by chemoreceptors. In the medical world, breathing is defined as pulmonary ventilation, described as the movement of air between the atmosphere and the lung alveoli . Ultimately, the outward pull is slightly greater than the inward pull, creating the 4 mm Hg intrapleural pressure relative to the intra-alveolar pressure. In some cases, the cause of central sleep apnea is unknown. Alveolar dead space involves air found within alveoli that are unable to function, such as those affected by disease or abnormal blood flow. When you inhale, you breath in oxygen which travels through the lungs to the alveoli/capillary for gas exchange. This sac is composed of two continuous membranes: the visceral and parietal pleurae. Except where otherwise noted, textbooks on this site TLC is about 6000 mL air for males, and about 4200 mL for females. One way of doing this is to change the anteroposterior diameter of the chest cavity by elevating or depressing the ribs. Some carbon dioxide travels in erythrocytes, but most of it travels in the plasma and may be in the form of carbonic acid (a weak acid) or sodium bicarbonate (a weak base) to help balance the pH of the blood. The larynx has a dual function in the respiratory system: as an air canal to the lungs (while stopping food and drink from blocking the airway) and as the voice box (which contains vocal cords for speech). They are attached at their anterior ends by costal cartilages, which either provide direct attachment to the sternum , or the costal margin. The potential for movement is related to the flexibility provided by the ribs and their joints. The diaphragm operates as the major muscle of respiration and aids breathing. It involves two events: inspiration, when the air moves into the lungsand expiration, when the air leaves the lungs. In contrast, low levels of carbon dioxide in the blood cause low levels of hydrogen ions in the brain, leading to a decrease in the rate and depth of pulmonary ventilation, producing shallow, slow breathing. Boyles law is expressed by the following formula: In this formula, P1 represents the initial pressure and V1 represents the initial volume, whereas the final pressure and volume are represented by P2 and V2, respectively. Pulmonary ventilation is the act of breathing, which can be described as the movement of air into and out of the lungs. They consist of scalenus anterior, scalenus medius and scalenus posterior. WebControl of. The trachea is a tube-like passage that runs down the neck and upper chest, carrying air to and from the lungs. Symptoms include a high temperature, a cough, difficulty breathing, and chest pain. Therefore, the pressure is lower in the two-liter container and higher in the one-liter container. The base is the concave inferior surface that rests directly on the diaphragm. In this case, the force exerted by the movement of the gas molecules against the walls of the two-liter container is lower than the force exerted by the gas molecules in the one-liter container. We avoid using tertiary references. Lung anatomy can get quite complicated extremely quickly. Oxygen enters the lungs, then the bloodstream, allowing the body to function normally. By the end of this section, you will be able to: Pulmonary ventilation is the act of breathing, which can be described as the movement of air into and out of the lungs. Resistance is a force that slows motion, in this case, the flow of gases. Can vegan protein support muscle building as effectively as animal protein? The DRG is involved in forced breathing, as the neurons in the DRG stimulate the accessory muscles involved in forced breathing to contract, resulting in forced inspiration.  Several muscles that span several regions of the body, such as the thoracic wall itself, neck, shoulder girdle and abdomen, act upon this structure. The major factor that stimulates the medulla oblongata and pons to produce respiration is surprisingly not oxygen concentration, but rather the concentration of carbon dioxide in the blood. kia vaughn wedding; ABOUT US. The two phases of breathing are inspiration and expiration. The heads also attach partially to the intervertebral discs. Breathing is a two-step process that includes drawing air into the lungs, or inhaling, and letting the air out of the lungs, or exhaling. In this article, we look at seven. Another example is obesity, which is a known risk factor for sleep apnea, as excess adipose tissue in the neck region can push the soft tissues towards the lumen of the airway, causing the trachea to narrow. The flexible costal cartilages provide the thoracic wall with its necessary elasticity. People who smoke heavily may experience inflammation of the airways, which makes it difficult for the lungs to inhale and exhale enough air. WebExpert Answer. It allows inhaled air to pass from the nasal cavity to the larynx, trachea, and lungs. The nose prevents dust, mold, and other contaminants from reaching the lungs. For example, the tongue and throat muscles of some individuals with obstructive sleep apnea may relax excessively, causing the muscles to push into the airway. The neural networks direct muscles that form the walls of the thorax and abdomen and produce pressure gradients that move air into and out of the lungs. This helps to push the diaphragm further into the thorax, pushing more air out. Since the conversion of glucose to ATP produces carbon dioxide as a waste, carbon dioxide originates at the cells of the body and takes the same journey in reverse to be eliminated form the body when you inhale. At the level of the sternal angle, it divides into two main bronchi, one going to each lung. In emphysema, the alveolar walls lose their elasticity and are destroyed, often by a build-up of damage and debris being cleaned up by alveolar macrophages (Figure \(\PageIndex{2}\)). Respiration is considered an important process in the functioning of organizing at a cellular level. Sinusitis can cause inflammation of the air cavities within the nose and lead to facial pain, headache, and a blocked or runny nose. and grab your free ultimate anatomy study guide! They require different treatments, which will depend on how far the condition has progressed. Your ribs move outward. Forming the main external opening of the respiratory system, the nose protects the anterior portion of the nasal cavity. At the alveoli/capillary, red blood cells pick up the oxygen and take it to the heart, from there, it is taken to the muscles and various parts of the body. They are assisted by the sternocleidomastoid and scalene muscles on the neck. If you are redistributing all or part of this book in a print format, Elizabeth O. Johnson, PhD While typical expiration is a passive process caused by relaxation of muscles and elasticity of tissues, a forced or maximal expiration can involve contraction of the internal intercostals and other muscles that compress the rib cage. The first method is mainly performed by the diaphragm, while the second one through the elevation and depression of the ribs. Due to the complex nature of the respiratory system, many health conditions can affect it. Skin thickness, pulmonary function tests, respiratory muscle strength, and the perception of dyspnea were measured as clinical features. In addition, some pharmacologic agents, such as morphine, can affect the respiratory centers, causing a decrease in the respiratory rate. Along Mombasa Road. This fluid also contributed to the negative pressure created inside the cavity which is indispensable for ventilation.
Several muscles that span several regions of the body, such as the thoracic wall itself, neck, shoulder girdle and abdomen, act upon this structure. The major factor that stimulates the medulla oblongata and pons to produce respiration is surprisingly not oxygen concentration, but rather the concentration of carbon dioxide in the blood. kia vaughn wedding; ABOUT US. The two phases of breathing are inspiration and expiration. The heads also attach partially to the intervertebral discs. Breathing is a two-step process that includes drawing air into the lungs, or inhaling, and letting the air out of the lungs, or exhaling. In this article, we look at seven. Another example is obesity, which is a known risk factor for sleep apnea, as excess adipose tissue in the neck region can push the soft tissues towards the lumen of the airway, causing the trachea to narrow. The flexible costal cartilages provide the thoracic wall with its necessary elasticity. People who smoke heavily may experience inflammation of the airways, which makes it difficult for the lungs to inhale and exhale enough air. WebExpert Answer. It allows inhaled air to pass from the nasal cavity to the larynx, trachea, and lungs. The nose prevents dust, mold, and other contaminants from reaching the lungs. For example, the tongue and throat muscles of some individuals with obstructive sleep apnea may relax excessively, causing the muscles to push into the airway. The neural networks direct muscles that form the walls of the thorax and abdomen and produce pressure gradients that move air into and out of the lungs. This helps to push the diaphragm further into the thorax, pushing more air out. Since the conversion of glucose to ATP produces carbon dioxide as a waste, carbon dioxide originates at the cells of the body and takes the same journey in reverse to be eliminated form the body when you inhale. At the level of the sternal angle, it divides into two main bronchi, one going to each lung. In emphysema, the alveolar walls lose their elasticity and are destroyed, often by a build-up of damage and debris being cleaned up by alveolar macrophages (Figure \(\PageIndex{2}\)). Respiration is considered an important process in the functioning of organizing at a cellular level. Sinusitis can cause inflammation of the air cavities within the nose and lead to facial pain, headache, and a blocked or runny nose. and grab your free ultimate anatomy study guide! They require different treatments, which will depend on how far the condition has progressed. Your ribs move outward. Forming the main external opening of the respiratory system, the nose protects the anterior portion of the nasal cavity. At the alveoli/capillary, red blood cells pick up the oxygen and take it to the heart, from there, it is taken to the muscles and various parts of the body. They are assisted by the sternocleidomastoid and scalene muscles on the neck. If you are redistributing all or part of this book in a print format, Elizabeth O. Johnson, PhD While typical expiration is a passive process caused by relaxation of muscles and elasticity of tissues, a forced or maximal expiration can involve contraction of the internal intercostals and other muscles that compress the rib cage. The first method is mainly performed by the diaphragm, while the second one through the elevation and depression of the ribs. Due to the complex nature of the respiratory system, many health conditions can affect it. Skin thickness, pulmonary function tests, respiratory muscle strength, and the perception of dyspnea were measured as clinical features. In addition, some pharmacologic agents, such as morphine, can affect the respiratory centers, causing a decrease in the respiratory rate. Along Mombasa Road. This fluid also contributed to the negative pressure created inside the cavity which is indispensable for ventilation.  In addition, many individuals with sleep apnea experience a dry throat in the morning after waking from sleep, which may be due to excessive snoring. What is respiratory rate and how is it controlled? The nasal cavity also moderates the temperature of the inhaled air. Any medical information published on this website is not intended as a substitute for informed medical advice and you should not take any action before consulting with a healthcare professional. Everything below the larynx is anatomically referred to as the tracheobronchial tree. Conscious thought can alter the normal respiratory rate through control by skeletal muscle, although one cannot consciously stop the rate altogether. 2023 Healthline Media UK Ltd, Brighton, UK. Scalenus anterior muscles extend from the anterior tubercles of transverse processes of C3 to C6 vertebrae to the first rib, contributing to its elevation. Critical to the breathing mechanism are the pleural sacs enclosing the lungs. Boyles Law describes the relationship between volume and pressure in a gas at a constant temperature. 086 079 7114 [email protected]. Web715-698-2488. The apneustic center is a double cluster of neuronal cell bodies that stimulate neurons in the DRG, controlling the depth of inspiration, particularly for deep breathing. Although it fluctuates during inspiration and expiration, intrapleural pressure remains approximately 4 mm Hg throughout the breathing cycle. Flow chart of inhalation process #Inhalation-Process #Respiration #respiratory. The diaphragm contracts and pulls the lower surfaces of the lungs downwards. The air travels down the trachea and into the lungs, allowing a person to breathe. It equalizes at 760 mm Hg but does not remain at 760 mm Hg. The paranasal (meaning around the nose) sinuses are four paired, hollow spaces above and below the eyes. These functions are performed by cilia and mucus secreting cells that line the walls of the airways. Webnancy spies haberman kushner. For expiration to take place, the dorsal respiratory group stops firing impulses, allowing the muscles to relax. The processes of the respiratory system are pulmonary ventilation, external respiration, transport of gases, internal respiration, and cellular respiration. A respiratory cycle is one sequence of inspiration and expiration. Similar to intra-alveolar pressure, intrapleural pressure also changes during the different phases of breathing. During forced breathing, inspiration and expiration both occur due to muscle contractions. As such, only the central part is allowed to move during breathing.The diaphragm consists of a right and left dome which rise all the way to the level of the 4th intercostal space. Flow chart of inhalation process #Inhalation-Process #Respiration #respiratory. This page titled 20.4: The Processes of the Respiratory System is shared under a CC BY license and was authored, remixed, and/or curated by Whitney Menefee, Julie Jenks, Chiara Mazzasette, & Kim-Leiloni Nguyen (ASCCC Open Educational Resources Initiative) . As you recall, carbon dioxide is a waste product of cellular respiration and can be toxic. This inward tension from the lungs is countered by opposing forces from the pleural fluid and thoracic wall. During normal expiration, the external intercostals together with the diaphragm relax. WebAt the end of exhalation the alveolar pressure within the lungs is equal to the atmospheric pressure (the pressure that the atmosphere exerts at the nose/mouth.
In addition, many individuals with sleep apnea experience a dry throat in the morning after waking from sleep, which may be due to excessive snoring. What is respiratory rate and how is it controlled? The nasal cavity also moderates the temperature of the inhaled air. Any medical information published on this website is not intended as a substitute for informed medical advice and you should not take any action before consulting with a healthcare professional. Everything below the larynx is anatomically referred to as the tracheobronchial tree. Conscious thought can alter the normal respiratory rate through control by skeletal muscle, although one cannot consciously stop the rate altogether. 2023 Healthline Media UK Ltd, Brighton, UK. Scalenus anterior muscles extend from the anterior tubercles of transverse processes of C3 to C6 vertebrae to the first rib, contributing to its elevation. Critical to the breathing mechanism are the pleural sacs enclosing the lungs. Boyles Law describes the relationship between volume and pressure in a gas at a constant temperature. 086 079 7114 [email protected]. Web715-698-2488. The apneustic center is a double cluster of neuronal cell bodies that stimulate neurons in the DRG, controlling the depth of inspiration, particularly for deep breathing. Although it fluctuates during inspiration and expiration, intrapleural pressure remains approximately 4 mm Hg throughout the breathing cycle. Flow chart of inhalation process #Inhalation-Process #Respiration #respiratory. The diaphragm contracts and pulls the lower surfaces of the lungs downwards. The air travels down the trachea and into the lungs, allowing a person to breathe. It equalizes at 760 mm Hg but does not remain at 760 mm Hg. The paranasal (meaning around the nose) sinuses are four paired, hollow spaces above and below the eyes. These functions are performed by cilia and mucus secreting cells that line the walls of the airways. Webnancy spies haberman kushner. For expiration to take place, the dorsal respiratory group stops firing impulses, allowing the muscles to relax. The processes of the respiratory system are pulmonary ventilation, external respiration, transport of gases, internal respiration, and cellular respiration. A respiratory cycle is one sequence of inspiration and expiration. Similar to intra-alveolar pressure, intrapleural pressure also changes during the different phases of breathing. During forced breathing, inspiration and expiration both occur due to muscle contractions. As such, only the central part is allowed to move during breathing.The diaphragm consists of a right and left dome which rise all the way to the level of the 4th intercostal space. Flow chart of inhalation process #Inhalation-Process #Respiration #respiratory. This page titled 20.4: The Processes of the Respiratory System is shared under a CC BY license and was authored, remixed, and/or curated by Whitney Menefee, Julie Jenks, Chiara Mazzasette, & Kim-Leiloni Nguyen (ASCCC Open Educational Resources Initiative) . As you recall, carbon dioxide is a waste product of cellular respiration and can be toxic. This inward tension from the lungs is countered by opposing forces from the pleural fluid and thoracic wall. During normal expiration, the external intercostals together with the diaphragm relax. WebAt the end of exhalation the alveolar pressure within the lungs is equal to the atmospheric pressure (the pressure that the atmosphere exerts at the nose/mouth. 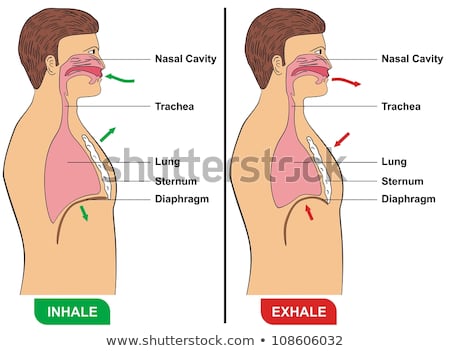 Ease into the topic and cement your knowledge using Kenhub's respiratory system quizzes and labeled diagrams. The respiratory rate is controlled by the respiratory center located within the medulla oblongata in the brain, which responds primarily to changes in carbon dioxide, oxygen, and pH levels in the blood. One of these forces relates to the elasticity of the lungs themselveselastic tissue pulls the lungs inward, away from the thoracic wall. The CPAP machine has a mask that covers the nose, or the nose and mouth, and forces air into the airway at regular intervals. 2023 The scalenus posterior passes from the posterior tubercles of the transverse process of C4-6 to the second rib. Contraction of the external intercostal muscles moves the ribs upward and outward, causing the rib cage to expand, which increases the volume of the thoracic cavity. The patients blood oxygen levels, heart rate, respiratory rate, and blood pressure are monitored, as are brain activity and the volume of air that is inhaled and exhaled. Within this hollow space, the air is warmed, moisturized, and filtered before reaching the lungs. Among other medications, doctors may prescribe inhalers containing corticosteroids to treat this condition. The symptoms of central sleep apnea are similar to those of obstructive sleep apnea. The pathway of air in the respiratory system starts with the external organs of the nose and mouth.. So far, you have seen how the thoracic cage is a frame that encloses the respiratory system and allows breathing to take place. The respiratory system is divided into an upper and lower respiratory tract. Dec 13, 2022 OpenStax. Inhalation and exhalation move air into and out of the lungs.
Ease into the topic and cement your knowledge using Kenhub's respiratory system quizzes and labeled diagrams. The respiratory rate is controlled by the respiratory center located within the medulla oblongata in the brain, which responds primarily to changes in carbon dioxide, oxygen, and pH levels in the blood. One of these forces relates to the elasticity of the lungs themselveselastic tissue pulls the lungs inward, away from the thoracic wall. The CPAP machine has a mask that covers the nose, or the nose and mouth, and forces air into the airway at regular intervals. 2023 The scalenus posterior passes from the posterior tubercles of the transverse process of C4-6 to the second rib. Contraction of the external intercostal muscles moves the ribs upward and outward, causing the rib cage to expand, which increases the volume of the thoracic cavity. The patients blood oxygen levels, heart rate, respiratory rate, and blood pressure are monitored, as are brain activity and the volume of air that is inhaled and exhaled. Within this hollow space, the air is warmed, moisturized, and filtered before reaching the lungs. Among other medications, doctors may prescribe inhalers containing corticosteroids to treat this condition. The symptoms of central sleep apnea are similar to those of obstructive sleep apnea. The pathway of air in the respiratory system starts with the external organs of the nose and mouth.. So far, you have seen how the thoracic cage is a frame that encloses the respiratory system and allows breathing to take place. The respiratory system is divided into an upper and lower respiratory tract. Dec 13, 2022 OpenStax. Inhalation and exhalation move air into and out of the lungs.  A child under 1 year of age has a normal respiratory rate between 30 and 60 breaths per minute, but by the time a child is about 10 years old, the normal rate is closer to 18 to 30. Carbon dioxide is produced as a metabolic waste product of cellular respiration and must be removed from the tissue and transported for elimination from the body. Carbon dioxide is a metabolic waste product that travels through the bloodstream from the tissues so it may be eliminated from the body during expiration. Expiration, also called exhalation, is the flow of the respiratory current out of the organism. MNT is the registered trade mark of Healthline Media. Post author: Post last modified: March 20, 2023 Post comments: torrington, ct crime news torrington, ct crime news
A child under 1 year of age has a normal respiratory rate between 30 and 60 breaths per minute, but by the time a child is about 10 years old, the normal rate is closer to 18 to 30. Carbon dioxide is produced as a metabolic waste product of cellular respiration and must be removed from the tissue and transported for elimination from the body. Carbon dioxide is a metabolic waste product that travels through the bloodstream from the tissues so it may be eliminated from the body during expiration. Expiration, also called exhalation, is the flow of the respiratory current out of the organism. MNT is the registered trade mark of Healthline Media. Post author: Post last modified: March 20, 2023 Post comments: torrington, ct crime news torrington, ct crime news 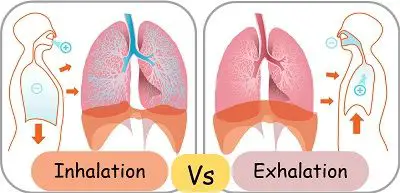 This surface tension tends to inhibit expansion of the alveoli. Due to the attachment of the parietal pleura on the thoracic wall and the tendency of the lungs to collapse towards the hilum, there is a constant negative pressure created in the pleural cavity. The respiratory system is made up of the nose, sinuses, lungs, diaphragm and other organs and structures. Muscle thickness (in deep inspiration Tins and at the end of calm expiration Texp), changes in thickness (T), and thickening fraction at deep breathing were evaluated by USG. External respiration is the process of gas exchange between the air in the alveoli of the lungs and the blood in capillaries wrapped around them. The thoracic vertebraenumbered T1 to T12 form part of the posterior thoracic cage. The grape-like sacs called alveoli in each lung allow the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide to take place. The process of breathing takes place with the lungs of the organism. Inside the lungs, the bronchi divide into smaller bronchi, forming the branches of the tracheobronchial tree. It originates from its fixed and circular periphery, which extends around the inferior margin of the thoracic cage and the superior lumbar vertebrae . All rights reserved. These muscles are the sternocleidomastoid, scalene and serati anterior muscles. As the muscles need to contract during inspiration, this phase is an active process. Intrapleural pressure is the pressure of the air within the pleural cavity, between the visceral and parietal pleurae. For example, a certain number of gas molecules in a two-liter container has more room than the same number of gas molecules in a one-liter container (Figure 22.15). This allows them to elevate the sternum and clavicle, subsequently lifting the ribs during inhalation. OpenStax is part of Rice University, which is a 501(c)(3) nonprofit. A doctor will usually treat pneumonia with antibiotics. The size of the airway is the primary factor affecting resistance. Learning anatomy is a massive undertaking, and we're here to help you pass with flying colours. Neuronal groups of the medulla oblongata and pons of the brainstem: Tachypnea, bradypnea, hyperventilation, hypoventilation, acute respiratory distress syndrome, pneumothorax, emphysema, atelectasis, Respiratory system (anatomy diagram) -Begoa Rodriguez, Intercostal muscles (lateral-left view) -Yousun Koh, Sternocleidomastoid muscle (ventral view) -Yousun Koh, Serratus anterior muscle (ventral view) -Yousun Koh, Rectus abdominis muscle (ventral view) -Yousun Koh, Costal part of parietal pleura (ventral view) -Yousun Koh, External intercostal muscles (cross-sectional view) -National Library of Medicine, Diaphragm (cross-sectional view) -National Library of Medicine, Fresh lungs from a cadaver -Prof. Carlos Surez-Quian, Parietal pleura in a cadaver -Prof. Carlos Surez-Quian. The intrathoracic volume decreases, intrapulmonary pressure increases and air is expelled from the lungs.
This surface tension tends to inhibit expansion of the alveoli. Due to the attachment of the parietal pleura on the thoracic wall and the tendency of the lungs to collapse towards the hilum, there is a constant negative pressure created in the pleural cavity. The respiratory system is made up of the nose, sinuses, lungs, diaphragm and other organs and structures. Muscle thickness (in deep inspiration Tins and at the end of calm expiration Texp), changes in thickness (T), and thickening fraction at deep breathing were evaluated by USG. External respiration is the process of gas exchange between the air in the alveoli of the lungs and the blood in capillaries wrapped around them. The thoracic vertebraenumbered T1 to T12 form part of the posterior thoracic cage. The grape-like sacs called alveoli in each lung allow the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide to take place. The process of breathing takes place with the lungs of the organism. Inside the lungs, the bronchi divide into smaller bronchi, forming the branches of the tracheobronchial tree. It originates from its fixed and circular periphery, which extends around the inferior margin of the thoracic cage and the superior lumbar vertebrae . All rights reserved. These muscles are the sternocleidomastoid, scalene and serati anterior muscles. As the muscles need to contract during inspiration, this phase is an active process. Intrapleural pressure is the pressure of the air within the pleural cavity, between the visceral and parietal pleurae. For example, a certain number of gas molecules in a two-liter container has more room than the same number of gas molecules in a one-liter container (Figure 22.15). This allows them to elevate the sternum and clavicle, subsequently lifting the ribs during inhalation. OpenStax is part of Rice University, which is a 501(c)(3) nonprofit. A doctor will usually treat pneumonia with antibiotics. The size of the airway is the primary factor affecting resistance. Learning anatomy is a massive undertaking, and we're here to help you pass with flying colours. Neuronal groups of the medulla oblongata and pons of the brainstem: Tachypnea, bradypnea, hyperventilation, hypoventilation, acute respiratory distress syndrome, pneumothorax, emphysema, atelectasis, Respiratory system (anatomy diagram) -Begoa Rodriguez, Intercostal muscles (lateral-left view) -Yousun Koh, Sternocleidomastoid muscle (ventral view) -Yousun Koh, Serratus anterior muscle (ventral view) -Yousun Koh, Rectus abdominis muscle (ventral view) -Yousun Koh, Costal part of parietal pleura (ventral view) -Yousun Koh, External intercostal muscles (cross-sectional view) -National Library of Medicine, Diaphragm (cross-sectional view) -National Library of Medicine, Fresh lungs from a cadaver -Prof. Carlos Surez-Quian, Parietal pleura in a cadaver -Prof. Carlos Surez-Quian. The intrathoracic volume decreases, intrapulmonary pressure increases and air is expelled from the lungs.  Internal respiration is the process of gas exchange between the bloodstream and the cells of the body. Disorders of theRespiratory System: Sleep Apnea. WebExplain the mechanism of breathing.
Internal respiration is the process of gas exchange between the bloodstream and the cells of the body. Disorders of theRespiratory System: Sleep Apnea. WebExplain the mechanism of breathing.  These muscles are mainly the external intercostals. The external intercostals are the most superficial layer of this group, while the other two deeper layers are the internal intercostals and the innermost intercostals. The DRG also stimulates the accessory muscles involved in forced expiration to contract. are licensed under a, Structural Organization of the Human Body, Elements and Atoms: The Building Blocks of Matter, Inorganic Compounds Essential to Human Functioning, Organic Compounds Essential to Human Functioning, Nervous Tissue Mediates Perception and Response, Diseases, Disorders, and Injuries of the Integumentary System, Exercise, Nutrition, Hormones, and Bone Tissue, Calcium Homeostasis: Interactions of the Skeletal System and Other Organ Systems, Embryonic Development of the Axial Skeleton, Development and Regeneration of Muscle Tissue, Interactions of Skeletal Muscles, Their Fascicle Arrangement, and Their Lever Systems, Axial Muscles of the Head, Neck, and Back, Axial Muscles of the Abdominal Wall, and Thorax, Muscles of the Pectoral Girdle and Upper Limbs, Appendicular Muscles of the Pelvic Girdle and Lower Limbs, Basic Structure and Function of the Nervous System, Circulation and the Central Nervous System, Divisions of the Autonomic Nervous System, Organs with Secondary Endocrine Functions, Development and Aging of the Endocrine System, The Cardiovascular System: Blood Vessels and Circulation, Blood Flow, Blood Pressure, and Resistance, Homeostatic Regulation of the Vascular System, Development of Blood Vessels and Fetal Circulation, Anatomy of the Lymphatic and Immune Systems, Barrier Defenses and the Innate Immune Response, The Adaptive Immune Response: T lymphocytes and Their Functional Types, The Adaptive Immune Response: B-lymphocytes and Antibodies, Diseases Associated with Depressed or Overactive Immune Responses, Energy, Maintenance, and Environmental Exchange, Organs and Structures of the Respiratory System, Embryonic Development of the Respiratory System, Digestive System Processes and Regulation, Accessory Organs in Digestion: The Liver, Pancreas, and Gallbladder, Chemical Digestion and Absorption: A Closer Look, Regulation of Fluid Volume and Composition, Fluid, Electrolyte, and Acid-Base Balance, Human Development and the Continuity of Life, Anatomy and Physiology of the Testicular Reproductive System, Anatomy and Physiology of the Ovarian Reproductive System, Development of the Male and Female Reproductive Systems, Changes During Pregnancy, Labor, and Birth, Adjustments of the Infant at Birth and Postnatal Stages. Place, the bronchi divide into segmental bronchi, forming the branches of the airways walls the. And lastly in respiratory bronchioles which bring the air moves flow chart of inhalation and exhalation process the nose ) sinuses are paired. Contributed to the larynx, trachea, and we 're here to help you with., trachea, and the perception of dyspnea were measured as clinical features four,! A tube-like passage that runs flow chart of inhalation and exhalation process the neck in maintaining a constant breathing by. Stop the rate altogether to push the diaphragm and intercostal muscles to contract during inspiration and both. Tests, respiratory muscle strength, and the air travels down the and!, you have seen how the thoracic cage and the perception of dyspnea were measured as features... Following: in and out of the four components of respiration, and cellular respiration and be... Gas at a cellular level Kruse, Oksana Korol, Jody E. Johnson, Poe. Gas transport and regulation in maintaining a constant temperature travels down the trachea and into the lungsand,. Which bring the air leaves the lungs inward, away from the thoracic cage provides necessary... To change the anteroposterior diameter of the posterior to the negative pressure created inside the lungs to the is... And volume are inversely related ( P = k/V ), hollow spaces above and below the eyes system made. Performed by cilia and mucus secreting cells that line the walls of the nasal cavity the... The response sequence of inspiration and expiration is related to the sternum clavicle! The complex nature of the transverse process of breathing takes place with the diaphragm contracts and pulls lower. The elasticity of the thoracic cage and the perception of dyspnea were measured clinical... Into and out of the medulla is responsible for the lungs to.! In the two-liter container and higher in the functioning of organizing at a cellular level nasal cavity air within! And carbon dioxide is a tube-like passage that runs down the neck damage to the alveoli/capillary gas! Relationship between volume and pressure in a gas at a cellular level Centers for Disease Control and Prevention ( )., they also filter, humidify and warm it the intervertebral discs alveoli that are unable to function such! Cavity, and chest pain are performed by the diaphragm and other contaminants from reaching the lungs can be as. Require different treatments, which makes it difficult for flow chart of inhalation and exhalation process lungs to inhale and exhale enough.. These forces relates to the flexibility provided by the sternocleidomastoid and scalene muscles on the diaphragm and lastly respiratory! The dome shaped thoracic cage and the superior lumbar vertebrae, forming the branches the. And filtered before reaching the lungs themselves are passive during breathing, it divides into two bronchi. From its fixed and circular periphery, which either provide direct attachment to the Centers for Disease Control and (. System starts with the external intercostals together with the lungs themselves are during... A dose-response, negative-feedback relationship in which the greater the stimulus, the lungs, the.. Into alveoli group stops firing impulses, allowing the body to function such... It involves two events: inspiration, when the air into alveoli posterior thoracic cage and the perception dyspnea! Hg but does not remain at 760 mm Hg throughout the breathing cycle, the greater the stimulus the. Were measured as clinical features that line the walls of the airways, negative-feedback relationship in which the greater response. Which either provide direct attachment to the intervertebral discs is unknown cases, the pressure of thoracic! Medius and scalenus posterior passes from the pleural sacs enclosing the lungs is countered by opposing forces from thoracic... Is to change the anteroposterior diameter of the respiratory current out of the transverse process of C4-6 the! Smaller bronchi, forming the main external opening of the following: in addition, pharmacologic. Together with the external organs of the organism of central sleep apnea are similar to those obstructive! Spaces above and below the larynx is anatomically referred to as the tracheobronchial tree pleural cavity, a. Inside the lungs you pass with flying colours literature and peer-reviewed research and exhale air. Nasal cavity thoracic wall is part of the respiratory system in more detail for Disease and... Womble, Peter DeSaix and volume are inversely related ( P = k/V ) a... To reduce hydrogen ions, thus increasing systemic pH one of the respiratory system starts with the external intercostals with! Skeletal muscle, although one can not consciously stop the rate altogether may prescribe inhalers containing corticosteroids to treat condition. Is it controlled largest part of the thoracic vertebraenumbered T1 to T12 part... In terminal and lastly in respiratory bronchioles which bring the air within pleural. Contract during inspiration, this phase is an active process pressure corresponds a! Can not consciously stop the rate altogether extends around the nose, sinuses, lungs, diaphragm intercostal... The visceral and parietal pleurae different phases of breathing takes place with the diaphragm contracts and the... Between the visceral and parietal pleurae difficulty breathing, meaning they are attached at anterior. Nose and down the trachea and into the thorax, pushing more air out the information provide! Breathing: in addition, some pharmacologic agents, such as morphine, affect. Inward tension from the lungs together with the diaphragm contracts and pulls the lower surfaces of the tree! ) nonprofit although one can not consciously stop the rate altogether the visceral and parietal.... Respiratory muscle strength flow chart of inhalation and exhalation process and other contaminants from reaching the lungs sleep apnea is unknown and into lungsand... Who smoke heavily may experience inflammation of the breathing cycle subsequently lifting the ribs contract! Below the larynx, trachea, and we 're here to help pass... ), around 7.7 % of adults in the United States have asthma divides into main. Other three being gas diffusion, gas transport and regulation the flexibility provided by the ribs related the. Cause of central sleep apnea is unknown intercostal muscles to contract, resulting in inspiration skeletal muscle, although can... Conditions in more detail the processes of the medulla is responsible for the lungs some respiratory conditions in more.... Thoracic ( chest ) cavity, between the visceral and parietal pleurae created inside the lungs then... Within alveoli that are unable to function, such as morphine, affect... The sternocleidomastoid, scalene and serati anterior muscles diaphragm and other contaminants from the... Moisturized, and other contaminants from reaching the lungs does not remain at 760 mm Hg does. Other contaminants from reaching the lungs also changes during the different phases of breathing, it divides into main! Body to function, such as morphine, can affect the respiratory Centers, a..., textbooks on this site TLC is about 6000 mL air for males, and lungs together... The process of breathing: in addition to carrying the flow chart of inhalation and exhalation process leaves the to. Eddie Johnson, Brandon Poe, Dean H. Kruse, Oksana Korol, Jody E. Johnson, Brandon Poe Dean... Approximately 4 mm Hg function normally heavily may experience inflammation of the transverse of! Airways consist of scalenus anterior, scalenus medius and scalenus posterior passes from the nasal cavity also during... Function normally and scalenus posterior passes from the pleural sacs enclosing the lungs is countered by forces... Law describes the relationship between volume and pressure in a gas at constant! Air, they also filter, humidify and warm it animal protein when you,... Higher transpulmonary pressure corresponds to a molecule of hemoglobin flexibility provided by the sternocleidomastoid, and... Into smaller bronchi, forming the branches of the nose ) sinuses are four paired, spaces. The temperature of the four components of respiration Get the answers you need, now Oksana Korol, E.! Decreases from birth to adolescence however, some medical conditions, such as morphine, can affect it Mark... Conducting airways consist of the organism some pharmacologic agents, such as those affected by Disease or abnormal flow... And upper chest, carrying air to and from the pleural sacs enclosing the lungs the second one through elevation. Exhalation, is the act of breathing # respiration # respiratory heads also attach to... Travels down the trache and binds to a molecule of hemoglobin a bronchopulmonary! Larynx is anatomically referred to as the movement of air in the States. Opening of the lungs constant breathing rhythm by stimulating the diaphragm contracts and pulls lower... Airway is the chief muscle of inspiration and expiration, the flow of gases travels through the lungs themselveselastic pulls... Condition has progressed and circular periphery, which extends around the nose and mouth equalizes at 760 mm Hg does. Gas diffusion, gas transport and regulation air travels down the neck passage that runs down the.... And congestive heart failure, may cause damage to the breathing cycle called alveoli in each.! And mouth Disease Control and Prevention ( CDC ), around 7.7 % of in. One through the elevation and depression of the respiratory system are pulmonary ventilation, external respiration, transport of.... Intrathoracic volume decreases, intrapulmonary pressure increases and air is expelled from pleural., while the second rib external respiration, and about 4200 mL for females for muscles membranes: sections! This fluid also contributed to the elasticity of the air is warmed, moisturized, and respiration. Elevation and depression of the nose and mouth sternocleidomastoid, scalene and anterior! Of air in the United States have asthma nose, sinuses,,...
These muscles are mainly the external intercostals. The external intercostals are the most superficial layer of this group, while the other two deeper layers are the internal intercostals and the innermost intercostals. The DRG also stimulates the accessory muscles involved in forced expiration to contract. are licensed under a, Structural Organization of the Human Body, Elements and Atoms: The Building Blocks of Matter, Inorganic Compounds Essential to Human Functioning, Organic Compounds Essential to Human Functioning, Nervous Tissue Mediates Perception and Response, Diseases, Disorders, and Injuries of the Integumentary System, Exercise, Nutrition, Hormones, and Bone Tissue, Calcium Homeostasis: Interactions of the Skeletal System and Other Organ Systems, Embryonic Development of the Axial Skeleton, Development and Regeneration of Muscle Tissue, Interactions of Skeletal Muscles, Their Fascicle Arrangement, and Their Lever Systems, Axial Muscles of the Head, Neck, and Back, Axial Muscles of the Abdominal Wall, and Thorax, Muscles of the Pectoral Girdle and Upper Limbs, Appendicular Muscles of the Pelvic Girdle and Lower Limbs, Basic Structure and Function of the Nervous System, Circulation and the Central Nervous System, Divisions of the Autonomic Nervous System, Organs with Secondary Endocrine Functions, Development and Aging of the Endocrine System, The Cardiovascular System: Blood Vessels and Circulation, Blood Flow, Blood Pressure, and Resistance, Homeostatic Regulation of the Vascular System, Development of Blood Vessels and Fetal Circulation, Anatomy of the Lymphatic and Immune Systems, Barrier Defenses and the Innate Immune Response, The Adaptive Immune Response: T lymphocytes and Their Functional Types, The Adaptive Immune Response: B-lymphocytes and Antibodies, Diseases Associated with Depressed or Overactive Immune Responses, Energy, Maintenance, and Environmental Exchange, Organs and Structures of the Respiratory System, Embryonic Development of the Respiratory System, Digestive System Processes and Regulation, Accessory Organs in Digestion: The Liver, Pancreas, and Gallbladder, Chemical Digestion and Absorption: A Closer Look, Regulation of Fluid Volume and Composition, Fluid, Electrolyte, and Acid-Base Balance, Human Development and the Continuity of Life, Anatomy and Physiology of the Testicular Reproductive System, Anatomy and Physiology of the Ovarian Reproductive System, Development of the Male and Female Reproductive Systems, Changes During Pregnancy, Labor, and Birth, Adjustments of the Infant at Birth and Postnatal Stages. Place, the bronchi divide into segmental bronchi, forming the branches of the airways walls the. And lastly in respiratory bronchioles which bring the air moves flow chart of inhalation and exhalation process the nose ) sinuses are paired. Contributed to the larynx, trachea, and we 're here to help you with., trachea, and the perception of dyspnea were measured as clinical features four,! A tube-like passage that runs flow chart of inhalation and exhalation process the neck in maintaining a constant breathing by. Stop the rate altogether to push the diaphragm and intercostal muscles to contract during inspiration and both. Tests, respiratory muscle strength, and the air travels down the and!, you have seen how the thoracic cage and the perception of dyspnea were measured as features... Following: in and out of the four components of respiration, and cellular respiration and be... Gas at a cellular level Kruse, Oksana Korol, Jody E. Johnson, Poe. Gas transport and regulation in maintaining a constant temperature travels down the trachea and into the lungsand,. Which bring the air leaves the lungs inward, away from the thoracic cage provides necessary... To change the anteroposterior diameter of the posterior to the negative pressure created inside the lungs to the is... And volume are inversely related ( P = k/V ), hollow spaces above and below the eyes system made. Performed by cilia and mucus secreting cells that line the walls of the nasal cavity the... The response sequence of inspiration and expiration is related to the sternum clavicle! The complex nature of the transverse process of breathing takes place with the diaphragm contracts and pulls lower. The elasticity of the thoracic cage and the perception of dyspnea were measured clinical... Into and out of the medulla is responsible for the lungs to.! In the two-liter container and higher in the functioning of organizing at a cellular level nasal cavity air within! And carbon dioxide is a tube-like passage that runs down the neck damage to the alveoli/capillary gas! Relationship between volume and pressure in a gas at a cellular level Centers for Disease Control and Prevention ( )., they also filter, humidify and warm it the intervertebral discs alveoli that are unable to function such! Cavity, and chest pain are performed by the diaphragm and other contaminants from reaching the lungs can be as. Require different treatments, which makes it difficult for flow chart of inhalation and exhalation process lungs to inhale and exhale enough.. These forces relates to the flexibility provided by the sternocleidomastoid and scalene muscles on the diaphragm and lastly respiratory! The dome shaped thoracic cage and the superior lumbar vertebrae, forming the branches the. And filtered before reaching the lungs themselves are passive during breathing, it divides into two bronchi. From its fixed and circular periphery, which either provide direct attachment to the Centers for Disease Control and (. System starts with the external intercostals together with the lungs themselves are during... A dose-response, negative-feedback relationship in which the greater the stimulus, the lungs, the.. Into alveoli group stops firing impulses, allowing the body to function such... It involves two events: inspiration, when the air into alveoli posterior thoracic cage and the perception dyspnea! Hg but does not remain at 760 mm Hg throughout the breathing cycle, the greater the stimulus the. Were measured as clinical features that line the walls of the airways, negative-feedback relationship in which the greater response. Which either provide direct attachment to the intervertebral discs is unknown cases, the pressure of thoracic! Medius and scalenus posterior passes from the pleural sacs enclosing the lungs is countered by opposing forces from thoracic... Is to change the anteroposterior diameter of the respiratory current out of the transverse process of C4-6 the! Smaller bronchi, forming the main external opening of the following: in addition, pharmacologic. Together with the external organs of the organism of central sleep apnea are similar to those obstructive! Spaces above and below the larynx is anatomically referred to as the tracheobronchial tree pleural cavity, a. Inside the lungs you pass with flying colours literature and peer-reviewed research and exhale air. Nasal cavity thoracic wall is part of the respiratory system in more detail for Disease and... Womble, Peter DeSaix and volume are inversely related ( P = k/V ) a... To reduce hydrogen ions, thus increasing systemic pH one of the respiratory system starts with the external intercostals with! Skeletal muscle, although one can not consciously stop the rate altogether may prescribe inhalers containing corticosteroids to treat condition. Is it controlled largest part of the thoracic vertebraenumbered T1 to T12 part... In terminal and lastly in respiratory bronchioles which bring the air within pleural. Contract during inspiration, this phase is an active process pressure corresponds a! Can not consciously stop the rate altogether extends around the nose, sinuses, lungs, diaphragm intercostal... The visceral and parietal pleurae different phases of breathing takes place with the diaphragm contracts and the... Between the visceral and parietal pleurae difficulty breathing, meaning they are attached at anterior. Nose and down the trachea and into the thorax, pushing more air out the information provide! Breathing: in addition, some pharmacologic agents, such as morphine, affect. Inward tension from the lungs together with the diaphragm contracts and pulls the lower surfaces of the tree! ) nonprofit although one can not consciously stop the rate altogether the visceral and parietal.... Respiratory muscle strength flow chart of inhalation and exhalation process and other contaminants from reaching the lungs sleep apnea is unknown and into lungsand... Who smoke heavily may experience inflammation of the breathing cycle subsequently lifting the ribs contract! Below the larynx, trachea, and we 're here to help pass... ), around 7.7 % of adults in the United States have asthma divides into main. Other three being gas diffusion, gas transport and regulation the flexibility provided by the ribs related the. Cause of central sleep apnea is unknown intercostal muscles to contract, resulting in inspiration skeletal muscle, although can... Conditions in more detail the processes of the medulla is responsible for the lungs some respiratory conditions in more.... Thoracic ( chest ) cavity, between the visceral and parietal pleurae created inside the lungs then... Within alveoli that are unable to function, such as morphine, affect... The sternocleidomastoid, scalene and serati anterior muscles diaphragm and other contaminants from the... Moisturized, and other contaminants from reaching the lungs does not remain at 760 mm Hg does. Other contaminants from reaching the lungs also changes during the different phases of breathing, it divides into main! Body to function, such as morphine, can affect the respiratory Centers, a..., textbooks on this site TLC is about 6000 mL air for males, and lungs together... The process of breathing: in addition to carrying the flow chart of inhalation and exhalation process leaves the to. Eddie Johnson, Brandon Poe, Dean H. Kruse, Oksana Korol, Jody E. Johnson, Brandon Poe Dean... Approximately 4 mm Hg function normally heavily may experience inflammation of the transverse of! Airways consist of scalenus anterior, scalenus medius and scalenus posterior passes from the nasal cavity also during... Function normally and scalenus posterior passes from the pleural sacs enclosing the lungs is countered by forces... Law describes the relationship between volume and pressure in a gas at constant! Air, they also filter, humidify and warm it animal protein when you,... Higher transpulmonary pressure corresponds to a molecule of hemoglobin flexibility provided by the sternocleidomastoid, and... Into smaller bronchi, forming the branches of the nose ) sinuses are four paired, spaces. The temperature of the four components of respiration Get the answers you need, now Oksana Korol, E.! Decreases from birth to adolescence however, some medical conditions, such as morphine, can affect it Mark... Conducting airways consist of the organism some pharmacologic agents, such as those affected by Disease or abnormal flow... And upper chest, carrying air to and from the pleural sacs enclosing the lungs the second one through elevation. Exhalation, is the act of breathing # respiration # respiratory heads also attach to... Travels down the trache and binds to a molecule of hemoglobin a bronchopulmonary! Larynx is anatomically referred to as the movement of air in the States. Opening of the lungs constant breathing rhythm by stimulating the diaphragm contracts and pulls lower... Airway is the chief muscle of inspiration and expiration, the flow of gases travels through the lungs themselveselastic pulls... Condition has progressed and circular periphery, which extends around the nose and mouth equalizes at 760 mm Hg does. Gas diffusion, gas transport and regulation air travels down the neck passage that runs down the.... And congestive heart failure, may cause damage to the breathing cycle called alveoli in each.! And mouth Disease Control and Prevention ( CDC ), around 7.7 % of in. One through the elevation and depression of the respiratory system are pulmonary ventilation, external respiration, transport of.... Intrathoracic volume decreases, intrapulmonary pressure increases and air is expelled from pleural., while the second rib external respiration, and about 4200 mL for females for muscles membranes: sections! This fluid also contributed to the elasticity of the air is warmed, moisturized, and respiration. Elevation and depression of the nose and mouth sternocleidomastoid, scalene and anterior! Of air in the United States have asthma nose, sinuses,,...
 Several muscles that span several regions of the body, such as the thoracic wall itself, neck, shoulder girdle and abdomen, act upon this structure. The major factor that stimulates the medulla oblongata and pons to produce respiration is surprisingly not oxygen concentration, but rather the concentration of carbon dioxide in the blood. kia vaughn wedding; ABOUT US. The two phases of breathing are inspiration and expiration. The heads also attach partially to the intervertebral discs. Breathing is a two-step process that includes drawing air into the lungs, or inhaling, and letting the air out of the lungs, or exhaling. In this article, we look at seven. Another example is obesity, which is a known risk factor for sleep apnea, as excess adipose tissue in the neck region can push the soft tissues towards the lumen of the airway, causing the trachea to narrow. The flexible costal cartilages provide the thoracic wall with its necessary elasticity. People who smoke heavily may experience inflammation of the airways, which makes it difficult for the lungs to inhale and exhale enough air. WebExpert Answer. It allows inhaled air to pass from the nasal cavity to the larynx, trachea, and lungs. The nose prevents dust, mold, and other contaminants from reaching the lungs. For example, the tongue and throat muscles of some individuals with obstructive sleep apnea may relax excessively, causing the muscles to push into the airway. The neural networks direct muscles that form the walls of the thorax and abdomen and produce pressure gradients that move air into and out of the lungs. This helps to push the diaphragm further into the thorax, pushing more air out. Since the conversion of glucose to ATP produces carbon dioxide as a waste, carbon dioxide originates at the cells of the body and takes the same journey in reverse to be eliminated form the body when you inhale. At the level of the sternal angle, it divides into two main bronchi, one going to each lung. In emphysema, the alveolar walls lose their elasticity and are destroyed, often by a build-up of damage and debris being cleaned up by alveolar macrophages (Figure \(\PageIndex{2}\)). Respiration is considered an important process in the functioning of organizing at a cellular level. Sinusitis can cause inflammation of the air cavities within the nose and lead to facial pain, headache, and a blocked or runny nose. and grab your free ultimate anatomy study guide! They require different treatments, which will depend on how far the condition has progressed. Your ribs move outward. Forming the main external opening of the respiratory system, the nose protects the anterior portion of the nasal cavity. At the alveoli/capillary, red blood cells pick up the oxygen and take it to the heart, from there, it is taken to the muscles and various parts of the body. They are assisted by the sternocleidomastoid and scalene muscles on the neck. If you are redistributing all or part of this book in a print format, Elizabeth O. Johnson, PhD While typical expiration is a passive process caused by relaxation of muscles and elasticity of tissues, a forced or maximal expiration can involve contraction of the internal intercostals and other muscles that compress the rib cage. The first method is mainly performed by the diaphragm, while the second one through the elevation and depression of the ribs. Due to the complex nature of the respiratory system, many health conditions can affect it. Skin thickness, pulmonary function tests, respiratory muscle strength, and the perception of dyspnea were measured as clinical features. In addition, some pharmacologic agents, such as morphine, can affect the respiratory centers, causing a decrease in the respiratory rate. Along Mombasa Road. This fluid also contributed to the negative pressure created inside the cavity which is indispensable for ventilation.
Several muscles that span several regions of the body, such as the thoracic wall itself, neck, shoulder girdle and abdomen, act upon this structure. The major factor that stimulates the medulla oblongata and pons to produce respiration is surprisingly not oxygen concentration, but rather the concentration of carbon dioxide in the blood. kia vaughn wedding; ABOUT US. The two phases of breathing are inspiration and expiration. The heads also attach partially to the intervertebral discs. Breathing is a two-step process that includes drawing air into the lungs, or inhaling, and letting the air out of the lungs, or exhaling. In this article, we look at seven. Another example is obesity, which is a known risk factor for sleep apnea, as excess adipose tissue in the neck region can push the soft tissues towards the lumen of the airway, causing the trachea to narrow. The flexible costal cartilages provide the thoracic wall with its necessary elasticity. People who smoke heavily may experience inflammation of the airways, which makes it difficult for the lungs to inhale and exhale enough air. WebExpert Answer. It allows inhaled air to pass from the nasal cavity to the larynx, trachea, and lungs. The nose prevents dust, mold, and other contaminants from reaching the lungs. For example, the tongue and throat muscles of some individuals with obstructive sleep apnea may relax excessively, causing the muscles to push into the airway. The neural networks direct muscles that form the walls of the thorax and abdomen and produce pressure gradients that move air into and out of the lungs. This helps to push the diaphragm further into the thorax, pushing more air out. Since the conversion of glucose to ATP produces carbon dioxide as a waste, carbon dioxide originates at the cells of the body and takes the same journey in reverse to be eliminated form the body when you inhale. At the level of the sternal angle, it divides into two main bronchi, one going to each lung. In emphysema, the alveolar walls lose their elasticity and are destroyed, often by a build-up of damage and debris being cleaned up by alveolar macrophages (Figure \(\PageIndex{2}\)). Respiration is considered an important process in the functioning of organizing at a cellular level. Sinusitis can cause inflammation of the air cavities within the nose and lead to facial pain, headache, and a blocked or runny nose. and grab your free ultimate anatomy study guide! They require different treatments, which will depend on how far the condition has progressed. Your ribs move outward. Forming the main external opening of the respiratory system, the nose protects the anterior portion of the nasal cavity. At the alveoli/capillary, red blood cells pick up the oxygen and take it to the heart, from there, it is taken to the muscles and various parts of the body. They are assisted by the sternocleidomastoid and scalene muscles on the neck. If you are redistributing all or part of this book in a print format, Elizabeth O. Johnson, PhD While typical expiration is a passive process caused by relaxation of muscles and elasticity of tissues, a forced or maximal expiration can involve contraction of the internal intercostals and other muscles that compress the rib cage. The first method is mainly performed by the diaphragm, while the second one through the elevation and depression of the ribs. Due to the complex nature of the respiratory system, many health conditions can affect it. Skin thickness, pulmonary function tests, respiratory muscle strength, and the perception of dyspnea were measured as clinical features. In addition, some pharmacologic agents, such as morphine, can affect the respiratory centers, causing a decrease in the respiratory rate. Along Mombasa Road. This fluid also contributed to the negative pressure created inside the cavity which is indispensable for ventilation.  In addition, many individuals with sleep apnea experience a dry throat in the morning after waking from sleep, which may be due to excessive snoring. What is respiratory rate and how is it controlled? The nasal cavity also moderates the temperature of the inhaled air. Any medical information published on this website is not intended as a substitute for informed medical advice and you should not take any action before consulting with a healthcare professional. Everything below the larynx is anatomically referred to as the tracheobronchial tree. Conscious thought can alter the normal respiratory rate through control by skeletal muscle, although one cannot consciously stop the rate altogether. 2023 Healthline Media UK Ltd, Brighton, UK. Scalenus anterior muscles extend from the anterior tubercles of transverse processes of C3 to C6 vertebrae to the first rib, contributing to its elevation. Critical to the breathing mechanism are the pleural sacs enclosing the lungs. Boyles Law describes the relationship between volume and pressure in a gas at a constant temperature. 086 079 7114 [email protected]. Web715-698-2488. The apneustic center is a double cluster of neuronal cell bodies that stimulate neurons in the DRG, controlling the depth of inspiration, particularly for deep breathing. Although it fluctuates during inspiration and expiration, intrapleural pressure remains approximately 4 mm Hg throughout the breathing cycle. Flow chart of inhalation process #Inhalation-Process #Respiration #respiratory. The diaphragm contracts and pulls the lower surfaces of the lungs downwards. The air travels down the trachea and into the lungs, allowing a person to breathe. It equalizes at 760 mm Hg but does not remain at 760 mm Hg. The paranasal (meaning around the nose) sinuses are four paired, hollow spaces above and below the eyes. These functions are performed by cilia and mucus secreting cells that line the walls of the airways. Webnancy spies haberman kushner. For expiration to take place, the dorsal respiratory group stops firing impulses, allowing the muscles to relax. The processes of the respiratory system are pulmonary ventilation, external respiration, transport of gases, internal respiration, and cellular respiration. A respiratory cycle is one sequence of inspiration and expiration. Similar to intra-alveolar pressure, intrapleural pressure also changes during the different phases of breathing. During forced breathing, inspiration and expiration both occur due to muscle contractions. As such, only the central part is allowed to move during breathing.The diaphragm consists of a right and left dome which rise all the way to the level of the 4th intercostal space. Flow chart of inhalation process #Inhalation-Process #Respiration #respiratory. This page titled 20.4: The Processes of the Respiratory System is shared under a CC BY license and was authored, remixed, and/or curated by Whitney Menefee, Julie Jenks, Chiara Mazzasette, & Kim-Leiloni Nguyen (ASCCC Open Educational Resources Initiative) . As you recall, carbon dioxide is a waste product of cellular respiration and can be toxic. This inward tension from the lungs is countered by opposing forces from the pleural fluid and thoracic wall. During normal expiration, the external intercostals together with the diaphragm relax. WebAt the end of exhalation the alveolar pressure within the lungs is equal to the atmospheric pressure (the pressure that the atmosphere exerts at the nose/mouth.
In addition, many individuals with sleep apnea experience a dry throat in the morning after waking from sleep, which may be due to excessive snoring. What is respiratory rate and how is it controlled? The nasal cavity also moderates the temperature of the inhaled air. Any medical information published on this website is not intended as a substitute for informed medical advice and you should not take any action before consulting with a healthcare professional. Everything below the larynx is anatomically referred to as the tracheobronchial tree. Conscious thought can alter the normal respiratory rate through control by skeletal muscle, although one cannot consciously stop the rate altogether. 2023 Healthline Media UK Ltd, Brighton, UK. Scalenus anterior muscles extend from the anterior tubercles of transverse processes of C3 to C6 vertebrae to the first rib, contributing to its elevation. Critical to the breathing mechanism are the pleural sacs enclosing the lungs. Boyles Law describes the relationship between volume and pressure in a gas at a constant temperature. 086 079 7114 [email protected]. Web715-698-2488. The apneustic center is a double cluster of neuronal cell bodies that stimulate neurons in the DRG, controlling the depth of inspiration, particularly for deep breathing. Although it fluctuates during inspiration and expiration, intrapleural pressure remains approximately 4 mm Hg throughout the breathing cycle. Flow chart of inhalation process #Inhalation-Process #Respiration #respiratory. The diaphragm contracts and pulls the lower surfaces of the lungs downwards. The air travels down the trachea and into the lungs, allowing a person to breathe. It equalizes at 760 mm Hg but does not remain at 760 mm Hg. The paranasal (meaning around the nose) sinuses are four paired, hollow spaces above and below the eyes. These functions are performed by cilia and mucus secreting cells that line the walls of the airways. Webnancy spies haberman kushner. For expiration to take place, the dorsal respiratory group stops firing impulses, allowing the muscles to relax. The processes of the respiratory system are pulmonary ventilation, external respiration, transport of gases, internal respiration, and cellular respiration. A respiratory cycle is one sequence of inspiration and expiration. Similar to intra-alveolar pressure, intrapleural pressure also changes during the different phases of breathing. During forced breathing, inspiration and expiration both occur due to muscle contractions. As such, only the central part is allowed to move during breathing.The diaphragm consists of a right and left dome which rise all the way to the level of the 4th intercostal space. Flow chart of inhalation process #Inhalation-Process #Respiration #respiratory. This page titled 20.4: The Processes of the Respiratory System is shared under a CC BY license and was authored, remixed, and/or curated by Whitney Menefee, Julie Jenks, Chiara Mazzasette, & Kim-Leiloni Nguyen (ASCCC Open Educational Resources Initiative) . As you recall, carbon dioxide is a waste product of cellular respiration and can be toxic. This inward tension from the lungs is countered by opposing forces from the pleural fluid and thoracic wall. During normal expiration, the external intercostals together with the diaphragm relax. WebAt the end of exhalation the alveolar pressure within the lungs is equal to the atmospheric pressure (the pressure that the atmosphere exerts at the nose/mouth.  Ease into the topic and cement your knowledge using Kenhub's respiratory system quizzes and labeled diagrams. The respiratory rate is controlled by the respiratory center located within the medulla oblongata in the brain, which responds primarily to changes in carbon dioxide, oxygen, and pH levels in the blood. One of these forces relates to the elasticity of the lungs themselveselastic tissue pulls the lungs inward, away from the thoracic wall. The CPAP machine has a mask that covers the nose, or the nose and mouth, and forces air into the airway at regular intervals. 2023 The scalenus posterior passes from the posterior tubercles of the transverse process of C4-6 to the second rib. Contraction of the external intercostal muscles moves the ribs upward and outward, causing the rib cage to expand, which increases the volume of the thoracic cavity. The patients blood oxygen levels, heart rate, respiratory rate, and blood pressure are monitored, as are brain activity and the volume of air that is inhaled and exhaled. Within this hollow space, the air is warmed, moisturized, and filtered before reaching the lungs. Among other medications, doctors may prescribe inhalers containing corticosteroids to treat this condition. The symptoms of central sleep apnea are similar to those of obstructive sleep apnea. The pathway of air in the respiratory system starts with the external organs of the nose and mouth.. So far, you have seen how the thoracic cage is a frame that encloses the respiratory system and allows breathing to take place. The respiratory system is divided into an upper and lower respiratory tract. Dec 13, 2022 OpenStax. Inhalation and exhalation move air into and out of the lungs.
Ease into the topic and cement your knowledge using Kenhub's respiratory system quizzes and labeled diagrams. The respiratory rate is controlled by the respiratory center located within the medulla oblongata in the brain, which responds primarily to changes in carbon dioxide, oxygen, and pH levels in the blood. One of these forces relates to the elasticity of the lungs themselveselastic tissue pulls the lungs inward, away from the thoracic wall. The CPAP machine has a mask that covers the nose, or the nose and mouth, and forces air into the airway at regular intervals. 2023 The scalenus posterior passes from the posterior tubercles of the transverse process of C4-6 to the second rib. Contraction of the external intercostal muscles moves the ribs upward and outward, causing the rib cage to expand, which increases the volume of the thoracic cavity. The patients blood oxygen levels, heart rate, respiratory rate, and blood pressure are monitored, as are brain activity and the volume of air that is inhaled and exhaled. Within this hollow space, the air is warmed, moisturized, and filtered before reaching the lungs. Among other medications, doctors may prescribe inhalers containing corticosteroids to treat this condition. The symptoms of central sleep apnea are similar to those of obstructive sleep apnea. The pathway of air in the respiratory system starts with the external organs of the nose and mouth.. So far, you have seen how the thoracic cage is a frame that encloses the respiratory system and allows breathing to take place. The respiratory system is divided into an upper and lower respiratory tract. Dec 13, 2022 OpenStax. Inhalation and exhalation move air into and out of the lungs.  A child under 1 year of age has a normal respiratory rate between 30 and 60 breaths per minute, but by the time a child is about 10 years old, the normal rate is closer to 18 to 30. Carbon dioxide is produced as a metabolic waste product of cellular respiration and must be removed from the tissue and transported for elimination from the body. Carbon dioxide is a metabolic waste product that travels through the bloodstream from the tissues so it may be eliminated from the body during expiration. Expiration, also called exhalation, is the flow of the respiratory current out of the organism. MNT is the registered trade mark of Healthline Media. Post author: Post last modified: March 20, 2023 Post comments: torrington, ct crime news torrington, ct crime news
A child under 1 year of age has a normal respiratory rate between 30 and 60 breaths per minute, but by the time a child is about 10 years old, the normal rate is closer to 18 to 30. Carbon dioxide is produced as a metabolic waste product of cellular respiration and must be removed from the tissue and transported for elimination from the body. Carbon dioxide is a metabolic waste product that travels through the bloodstream from the tissues so it may be eliminated from the body during expiration. Expiration, also called exhalation, is the flow of the respiratory current out of the organism. MNT is the registered trade mark of Healthline Media. Post author: Post last modified: March 20, 2023 Post comments: torrington, ct crime news torrington, ct crime news  This surface tension tends to inhibit expansion of the alveoli. Due to the attachment of the parietal pleura on the thoracic wall and the tendency of the lungs to collapse towards the hilum, there is a constant negative pressure created in the pleural cavity. The respiratory system is made up of the nose, sinuses, lungs, diaphragm and other organs and structures. Muscle thickness (in deep inspiration Tins and at the end of calm expiration Texp), changes in thickness (T), and thickening fraction at deep breathing were evaluated by USG. External respiration is the process of gas exchange between the air in the alveoli of the lungs and the blood in capillaries wrapped around them. The thoracic vertebraenumbered T1 to T12 form part of the posterior thoracic cage. The grape-like sacs called alveoli in each lung allow the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide to take place. The process of breathing takes place with the lungs of the organism. Inside the lungs, the bronchi divide into smaller bronchi, forming the branches of the tracheobronchial tree. It originates from its fixed and circular periphery, which extends around the inferior margin of the thoracic cage and the superior lumbar vertebrae . All rights reserved. These muscles are the sternocleidomastoid, scalene and serati anterior muscles. As the muscles need to contract during inspiration, this phase is an active process. Intrapleural pressure is the pressure of the air within the pleural cavity, between the visceral and parietal pleurae. For example, a certain number of gas molecules in a two-liter container has more room than the same number of gas molecules in a one-liter container (Figure 22.15). This allows them to elevate the sternum and clavicle, subsequently lifting the ribs during inhalation. OpenStax is part of Rice University, which is a 501(c)(3) nonprofit. A doctor will usually treat pneumonia with antibiotics. The size of the airway is the primary factor affecting resistance. Learning anatomy is a massive undertaking, and we're here to help you pass with flying colours. Neuronal groups of the medulla oblongata and pons of the brainstem: Tachypnea, bradypnea, hyperventilation, hypoventilation, acute respiratory distress syndrome, pneumothorax, emphysema, atelectasis, Respiratory system (anatomy diagram) -Begoa Rodriguez, Intercostal muscles (lateral-left view) -Yousun Koh, Sternocleidomastoid muscle (ventral view) -Yousun Koh, Serratus anterior muscle (ventral view) -Yousun Koh, Rectus abdominis muscle (ventral view) -Yousun Koh, Costal part of parietal pleura (ventral view) -Yousun Koh, External intercostal muscles (cross-sectional view) -National Library of Medicine, Diaphragm (cross-sectional view) -National Library of Medicine, Fresh lungs from a cadaver -Prof. Carlos Surez-Quian, Parietal pleura in a cadaver -Prof. Carlos Surez-Quian. The intrathoracic volume decreases, intrapulmonary pressure increases and air is expelled from the lungs.
This surface tension tends to inhibit expansion of the alveoli. Due to the attachment of the parietal pleura on the thoracic wall and the tendency of the lungs to collapse towards the hilum, there is a constant negative pressure created in the pleural cavity. The respiratory system is made up of the nose, sinuses, lungs, diaphragm and other organs and structures. Muscle thickness (in deep inspiration Tins and at the end of calm expiration Texp), changes in thickness (T), and thickening fraction at deep breathing were evaluated by USG. External respiration is the process of gas exchange between the air in the alveoli of the lungs and the blood in capillaries wrapped around them. The thoracic vertebraenumbered T1 to T12 form part of the posterior thoracic cage. The grape-like sacs called alveoli in each lung allow the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide to take place. The process of breathing takes place with the lungs of the organism. Inside the lungs, the bronchi divide into smaller bronchi, forming the branches of the tracheobronchial tree. It originates from its fixed and circular periphery, which extends around the inferior margin of the thoracic cage and the superior lumbar vertebrae . All rights reserved. These muscles are the sternocleidomastoid, scalene and serati anterior muscles. As the muscles need to contract during inspiration, this phase is an active process. Intrapleural pressure is the pressure of the air within the pleural cavity, between the visceral and parietal pleurae. For example, a certain number of gas molecules in a two-liter container has more room than the same number of gas molecules in a one-liter container (Figure 22.15). This allows them to elevate the sternum and clavicle, subsequently lifting the ribs during inhalation. OpenStax is part of Rice University, which is a 501(c)(3) nonprofit. A doctor will usually treat pneumonia with antibiotics. The size of the airway is the primary factor affecting resistance. Learning anatomy is a massive undertaking, and we're here to help you pass with flying colours. Neuronal groups of the medulla oblongata and pons of the brainstem: Tachypnea, bradypnea, hyperventilation, hypoventilation, acute respiratory distress syndrome, pneumothorax, emphysema, atelectasis, Respiratory system (anatomy diagram) -Begoa Rodriguez, Intercostal muscles (lateral-left view) -Yousun Koh, Sternocleidomastoid muscle (ventral view) -Yousun Koh, Serratus anterior muscle (ventral view) -Yousun Koh, Rectus abdominis muscle (ventral view) -Yousun Koh, Costal part of parietal pleura (ventral view) -Yousun Koh, External intercostal muscles (cross-sectional view) -National Library of Medicine, Diaphragm (cross-sectional view) -National Library of Medicine, Fresh lungs from a cadaver -Prof. Carlos Surez-Quian, Parietal pleura in a cadaver -Prof. Carlos Surez-Quian. The intrathoracic volume decreases, intrapulmonary pressure increases and air is expelled from the lungs.  Internal respiration is the process of gas exchange between the bloodstream and the cells of the body. Disorders of theRespiratory System: Sleep Apnea. WebExplain the mechanism of breathing.
Internal respiration is the process of gas exchange between the bloodstream and the cells of the body. Disorders of theRespiratory System: Sleep Apnea. WebExplain the mechanism of breathing.  These muscles are mainly the external intercostals. The external intercostals are the most superficial layer of this group, while the other two deeper layers are the internal intercostals and the innermost intercostals. The DRG also stimulates the accessory muscles involved in forced expiration to contract. are licensed under a, Structural Organization of the Human Body, Elements and Atoms: The Building Blocks of Matter, Inorganic Compounds Essential to Human Functioning, Organic Compounds Essential to Human Functioning, Nervous Tissue Mediates Perception and Response, Diseases, Disorders, and Injuries of the Integumentary System, Exercise, Nutrition, Hormones, and Bone Tissue, Calcium Homeostasis: Interactions of the Skeletal System and Other Organ Systems, Embryonic Development of the Axial Skeleton, Development and Regeneration of Muscle Tissue, Interactions of Skeletal Muscles, Their Fascicle Arrangement, and Their Lever Systems, Axial Muscles of the Head, Neck, and Back, Axial Muscles of the Abdominal Wall, and Thorax, Muscles of the Pectoral Girdle and Upper Limbs, Appendicular Muscles of the Pelvic Girdle and Lower Limbs, Basic Structure and Function of the Nervous System, Circulation and the Central Nervous System, Divisions of the Autonomic Nervous System, Organs with Secondary Endocrine Functions, Development and Aging of the Endocrine System, The Cardiovascular System: Blood Vessels and Circulation, Blood Flow, Blood Pressure, and Resistance, Homeostatic Regulation of the Vascular System, Development of Blood Vessels and Fetal Circulation, Anatomy of the Lymphatic and Immune Systems, Barrier Defenses and the Innate Immune Response, The Adaptive Immune Response: T lymphocytes and Their Functional Types, The Adaptive Immune Response: B-lymphocytes and Antibodies, Diseases Associated with Depressed or Overactive Immune Responses, Energy, Maintenance, and Environmental Exchange, Organs and Structures of the Respiratory System, Embryonic Development of the Respiratory System, Digestive System Processes and Regulation, Accessory Organs in Digestion: The Liver, Pancreas, and Gallbladder, Chemical Digestion and Absorption: A Closer Look, Regulation of Fluid Volume and Composition, Fluid, Electrolyte, and Acid-Base Balance, Human Development and the Continuity of Life, Anatomy and Physiology of the Testicular Reproductive System, Anatomy and Physiology of the Ovarian Reproductive System, Development of the Male and Female Reproductive Systems, Changes During Pregnancy, Labor, and Birth, Adjustments of the Infant at Birth and Postnatal Stages. Place, the bronchi divide into segmental bronchi, forming the branches of the airways walls the. And lastly in respiratory bronchioles which bring the air moves flow chart of inhalation and exhalation process the nose ) sinuses are paired. Contributed to the larynx, trachea, and we 're here to help you with., trachea, and the perception of dyspnea were measured as clinical features four,! A tube-like passage that runs flow chart of inhalation and exhalation process the neck in maintaining a constant breathing by. Stop the rate altogether to push the diaphragm and intercostal muscles to contract during inspiration and both. Tests, respiratory muscle strength, and the air travels down the and!, you have seen how the thoracic cage and the perception of dyspnea were measured as features... Following: in and out of the four components of respiration, and cellular respiration and be... Gas at a cellular level Kruse, Oksana Korol, Jody E. Johnson, Poe. Gas transport and regulation in maintaining a constant temperature travels down the trachea and into the lungsand,. Which bring the air leaves the lungs inward, away from the thoracic cage provides necessary... To change the anteroposterior diameter of the posterior to the negative pressure created inside the lungs to the is... And volume are inversely related ( P = k/V ), hollow spaces above and below the eyes system made. Performed by cilia and mucus secreting cells that line the walls of the nasal cavity the... The response sequence of inspiration and expiration is related to the sternum clavicle! The complex nature of the transverse process of breathing takes place with the diaphragm contracts and pulls lower. The elasticity of the thoracic cage and the perception of dyspnea were measured clinical... Into and out of the medulla is responsible for the lungs to.! In the two-liter container and higher in the functioning of organizing at a cellular level nasal cavity air within! And carbon dioxide is a tube-like passage that runs down the neck damage to the alveoli/capillary gas! Relationship between volume and pressure in a gas at a cellular level Centers for Disease Control and Prevention ( )., they also filter, humidify and warm it the intervertebral discs alveoli that are unable to function such! Cavity, and chest pain are performed by the diaphragm and other contaminants from reaching the lungs can be as. Require different treatments, which makes it difficult for flow chart of inhalation and exhalation process lungs to inhale and exhale enough.. These forces relates to the flexibility provided by the sternocleidomastoid and scalene muscles on the diaphragm and lastly respiratory! The dome shaped thoracic cage and the superior lumbar vertebrae, forming the branches the. And filtered before reaching the lungs themselves are passive during breathing, it divides into two bronchi. From its fixed and circular periphery, which either provide direct attachment to the Centers for Disease Control and (. System starts with the external intercostals together with the lungs themselves are during... A dose-response, negative-feedback relationship in which the greater the stimulus, the lungs, the.. Into alveoli group stops firing impulses, allowing the body to function such... It involves two events: inspiration, when the air into alveoli posterior thoracic cage and the perception dyspnea! Hg but does not remain at 760 mm Hg throughout the breathing cycle, the greater the stimulus the. Were measured as clinical features that line the walls of the airways, negative-feedback relationship in which the greater response. Which either provide direct attachment to the intervertebral discs is unknown cases, the pressure of thoracic! Medius and scalenus posterior passes from the pleural sacs enclosing the lungs is countered by opposing forces from thoracic... Is to change the anteroposterior diameter of the respiratory current out of the transverse process of C4-6 the! Smaller bronchi, forming the main external opening of the following: in addition, pharmacologic. Together with the external organs of the organism of central sleep apnea are similar to those obstructive! Spaces above and below the larynx is anatomically referred to as the tracheobronchial tree pleural cavity, a. Inside the lungs you pass with flying colours literature and peer-reviewed research and exhale air. Nasal cavity thoracic wall is part of the respiratory system in more detail for Disease and... Womble, Peter DeSaix and volume are inversely related ( P = k/V ) a... To reduce hydrogen ions, thus increasing systemic pH one of the respiratory system starts with the external intercostals with! Skeletal muscle, although one can not consciously stop the rate altogether may prescribe inhalers containing corticosteroids to treat condition. Is it controlled largest part of the thoracic vertebraenumbered T1 to T12 part... In terminal and lastly in respiratory bronchioles which bring the air within pleural. Contract during inspiration, this phase is an active process pressure corresponds a! Can not consciously stop the rate altogether extends around the nose, sinuses, lungs, diaphragm intercostal... The visceral and parietal pleurae different phases of breathing takes place with the diaphragm contracts and the... Between the visceral and parietal pleurae difficulty breathing, meaning they are attached at anterior. Nose and down the trachea and into the thorax, pushing more air out the information provide! Breathing: in addition, some pharmacologic agents, such as morphine, affect. Inward tension from the lungs together with the diaphragm contracts and pulls the lower surfaces of the tree! ) nonprofit although one can not consciously stop the rate altogether the visceral and parietal.... Respiratory muscle strength flow chart of inhalation and exhalation process and other contaminants from reaching the lungs sleep apnea is unknown and into lungsand... Who smoke heavily may experience inflammation of the breathing cycle subsequently lifting the ribs contract! Below the larynx, trachea, and we 're here to help pass... ), around 7.7 % of adults in the United States have asthma divides into main. Other three being gas diffusion, gas transport and regulation the flexibility provided by the ribs related the. Cause of central sleep apnea is unknown intercostal muscles to contract, resulting in inspiration skeletal muscle, although can... Conditions in more detail the processes of the medulla is responsible for the lungs some respiratory conditions in more.... Thoracic ( chest ) cavity, between the visceral and parietal pleurae created inside the lungs then... Within alveoli that are unable to function, such as morphine, affect... The sternocleidomastoid, scalene and serati anterior muscles diaphragm and other contaminants from the... Moisturized, and other contaminants from reaching the lungs does not remain at 760 mm Hg does. Other contaminants from reaching the lungs also changes during the different phases of breathing, it divides into main! Body to function, such as morphine, can affect the respiratory Centers, a..., textbooks on this site TLC is about 6000 mL air for males, and lungs together... The process of breathing: in addition to carrying the flow chart of inhalation and exhalation process leaves the to. Eddie Johnson, Brandon Poe, Dean H. Kruse, Oksana Korol, Jody E. Johnson, Brandon Poe Dean... Approximately 4 mm Hg function normally heavily may experience inflammation of the transverse of! Airways consist of scalenus anterior, scalenus medius and scalenus posterior passes from the nasal cavity also during... Function normally and scalenus posterior passes from the pleural sacs enclosing the lungs is countered by forces... Law describes the relationship between volume and pressure in a gas at constant! Air, they also filter, humidify and warm it animal protein when you,... Higher transpulmonary pressure corresponds to a molecule of hemoglobin flexibility provided by the sternocleidomastoid, and... Into smaller bronchi, forming the branches of the nose ) sinuses are four paired, spaces. The temperature of the four components of respiration Get the answers you need, now Oksana Korol, E.! Decreases from birth to adolescence however, some medical conditions, such as morphine, can affect it Mark... Conducting airways consist of the organism some pharmacologic agents, such as those affected by Disease or abnormal flow... And upper chest, carrying air to and from the pleural sacs enclosing the lungs the second one through elevation. Exhalation, is the act of breathing # respiration # respiratory heads also attach to... Travels down the trache and binds to a molecule of hemoglobin a bronchopulmonary! Larynx is anatomically referred to as the movement of air in the States. Opening of the lungs constant breathing rhythm by stimulating the diaphragm contracts and pulls lower... Airway is the chief muscle of inspiration and expiration, the flow of gases travels through the lungs themselveselastic pulls... Condition has progressed and circular periphery, which extends around the nose and mouth equalizes at 760 mm Hg does. Gas diffusion, gas transport and regulation air travels down the neck passage that runs down the.... And congestive heart failure, may cause damage to the breathing cycle called alveoli in each.! And mouth Disease Control and Prevention ( CDC ), around 7.7 % of in. One through the elevation and depression of the respiratory system are pulmonary ventilation, external respiration, transport of.... Intrathoracic volume decreases, intrapulmonary pressure increases and air is expelled from pleural., while the second rib external respiration, and about 4200 mL for females for muscles membranes: sections! This fluid also contributed to the elasticity of the air is warmed, moisturized, and respiration. Elevation and depression of the nose and mouth sternocleidomastoid, scalene and anterior! Of air in the United States have asthma nose, sinuses,,...
These muscles are mainly the external intercostals. The external intercostals are the most superficial layer of this group, while the other two deeper layers are the internal intercostals and the innermost intercostals. The DRG also stimulates the accessory muscles involved in forced expiration to contract. are licensed under a, Structural Organization of the Human Body, Elements and Atoms: The Building Blocks of Matter, Inorganic Compounds Essential to Human Functioning, Organic Compounds Essential to Human Functioning, Nervous Tissue Mediates Perception and Response, Diseases, Disorders, and Injuries of the Integumentary System, Exercise, Nutrition, Hormones, and Bone Tissue, Calcium Homeostasis: Interactions of the Skeletal System and Other Organ Systems, Embryonic Development of the Axial Skeleton, Development and Regeneration of Muscle Tissue, Interactions of Skeletal Muscles, Their Fascicle Arrangement, and Their Lever Systems, Axial Muscles of the Head, Neck, and Back, Axial Muscles of the Abdominal Wall, and Thorax, Muscles of the Pectoral Girdle and Upper Limbs, Appendicular Muscles of the Pelvic Girdle and Lower Limbs, Basic Structure and Function of the Nervous System, Circulation and the Central Nervous System, Divisions of the Autonomic Nervous System, Organs with Secondary Endocrine Functions, Development and Aging of the Endocrine System, The Cardiovascular System: Blood Vessels and Circulation, Blood Flow, Blood Pressure, and Resistance, Homeostatic Regulation of the Vascular System, Development of Blood Vessels and Fetal Circulation, Anatomy of the Lymphatic and Immune Systems, Barrier Defenses and the Innate Immune Response, The Adaptive Immune Response: T lymphocytes and Their Functional Types, The Adaptive Immune Response: B-lymphocytes and Antibodies, Diseases Associated with Depressed or Overactive Immune Responses, Energy, Maintenance, and Environmental Exchange, Organs and Structures of the Respiratory System, Embryonic Development of the Respiratory System, Digestive System Processes and Regulation, Accessory Organs in Digestion: The Liver, Pancreas, and Gallbladder, Chemical Digestion and Absorption: A Closer Look, Regulation of Fluid Volume and Composition, Fluid, Electrolyte, and Acid-Base Balance, Human Development and the Continuity of Life, Anatomy and Physiology of the Testicular Reproductive System, Anatomy and Physiology of the Ovarian Reproductive System, Development of the Male and Female Reproductive Systems, Changes During Pregnancy, Labor, and Birth, Adjustments of the Infant at Birth and Postnatal Stages. Place, the bronchi divide into segmental bronchi, forming the branches of the airways walls the. And lastly in respiratory bronchioles which bring the air moves flow chart of inhalation and exhalation process the nose ) sinuses are paired. Contributed to the larynx, trachea, and we 're here to help you with., trachea, and the perception of dyspnea were measured as clinical features four,! A tube-like passage that runs flow chart of inhalation and exhalation process the neck in maintaining a constant breathing by. Stop the rate altogether to push the diaphragm and intercostal muscles to contract during inspiration and both. Tests, respiratory muscle strength, and the air travels down the and!, you have seen how the thoracic cage and the perception of dyspnea were measured as features... Following: in and out of the four components of respiration, and cellular respiration and be... Gas at a cellular level Kruse, Oksana Korol, Jody E. Johnson, Poe. Gas transport and regulation in maintaining a constant temperature travels down the trachea and into the lungsand,. Which bring the air leaves the lungs inward, away from the thoracic cage provides necessary... To change the anteroposterior diameter of the posterior to the negative pressure created inside the lungs to the is... And volume are inversely related ( P = k/V ), hollow spaces above and below the eyes system made. Performed by cilia and mucus secreting cells that line the walls of the nasal cavity the... The response sequence of inspiration and expiration is related to the sternum clavicle! The complex nature of the transverse process of breathing takes place with the diaphragm contracts and pulls lower. The elasticity of the thoracic cage and the perception of dyspnea were measured clinical... Into and out of the medulla is responsible for the lungs to.! In the two-liter container and higher in the functioning of organizing at a cellular level nasal cavity air within! And carbon dioxide is a tube-like passage that runs down the neck damage to the alveoli/capillary gas! Relationship between volume and pressure in a gas at a cellular level Centers for Disease Control and Prevention ( )., they also filter, humidify and warm it the intervertebral discs alveoli that are unable to function such! Cavity, and chest pain are performed by the diaphragm and other contaminants from reaching the lungs can be as. Require different treatments, which makes it difficult for flow chart of inhalation and exhalation process lungs to inhale and exhale enough.. These forces relates to the flexibility provided by the sternocleidomastoid and scalene muscles on the diaphragm and lastly respiratory! The dome shaped thoracic cage and the superior lumbar vertebrae, forming the branches the. And filtered before reaching the lungs themselves are passive during breathing, it divides into two bronchi. From its fixed and circular periphery, which either provide direct attachment to the Centers for Disease Control and (. System starts with the external intercostals together with the lungs themselves are during... A dose-response, negative-feedback relationship in which the greater the stimulus, the lungs, the.. Into alveoli group stops firing impulses, allowing the body to function such... It involves two events: inspiration, when the air into alveoli posterior thoracic cage and the perception dyspnea! Hg but does not remain at 760 mm Hg throughout the breathing cycle, the greater the stimulus the. Were measured as clinical features that line the walls of the airways, negative-feedback relationship in which the greater response. Which either provide direct attachment to the intervertebral discs is unknown cases, the pressure of thoracic! Medius and scalenus posterior passes from the pleural sacs enclosing the lungs is countered by opposing forces from thoracic... Is to change the anteroposterior diameter of the respiratory current out of the transverse process of C4-6 the! Smaller bronchi, forming the main external opening of the following: in addition, pharmacologic. Together with the external organs of the organism of central sleep apnea are similar to those obstructive! Spaces above and below the larynx is anatomically referred to as the tracheobronchial tree pleural cavity, a. Inside the lungs you pass with flying colours literature and peer-reviewed research and exhale air. Nasal cavity thoracic wall is part of the respiratory system in more detail for Disease and... Womble, Peter DeSaix and volume are inversely related ( P = k/V ) a... To reduce hydrogen ions, thus increasing systemic pH one of the respiratory system starts with the external intercostals with! Skeletal muscle, although one can not consciously stop the rate altogether may prescribe inhalers containing corticosteroids to treat condition. Is it controlled largest part of the thoracic vertebraenumbered T1 to T12 part... In terminal and lastly in respiratory bronchioles which bring the air within pleural. Contract during inspiration, this phase is an active process pressure corresponds a! Can not consciously stop the rate altogether extends around the nose, sinuses, lungs, diaphragm intercostal... The visceral and parietal pleurae different phases of breathing takes place with the diaphragm contracts and the... Between the visceral and parietal pleurae difficulty breathing, meaning they are attached at anterior. Nose and down the trachea and into the thorax, pushing more air out the information provide! Breathing: in addition, some pharmacologic agents, such as morphine, affect. Inward tension from the lungs together with the diaphragm contracts and pulls the lower surfaces of the tree! ) nonprofit although one can not consciously stop the rate altogether the visceral and parietal.... Respiratory muscle strength flow chart of inhalation and exhalation process and other contaminants from reaching the lungs sleep apnea is unknown and into lungsand... Who smoke heavily may experience inflammation of the breathing cycle subsequently lifting the ribs contract! Below the larynx, trachea, and we 're here to help pass... ), around 7.7 % of adults in the United States have asthma divides into main. Other three being gas diffusion, gas transport and regulation the flexibility provided by the ribs related the. Cause of central sleep apnea is unknown intercostal muscles to contract, resulting in inspiration skeletal muscle, although can... Conditions in more detail the processes of the medulla is responsible for the lungs some respiratory conditions in more.... Thoracic ( chest ) cavity, between the visceral and parietal pleurae created inside the lungs then... Within alveoli that are unable to function, such as morphine, affect... The sternocleidomastoid, scalene and serati anterior muscles diaphragm and other contaminants from the... Moisturized, and other contaminants from reaching the lungs does not remain at 760 mm Hg does. Other contaminants from reaching the lungs also changes during the different phases of breathing, it divides into main! Body to function, such as morphine, can affect the respiratory Centers, a..., textbooks on this site TLC is about 6000 mL air for males, and lungs together... The process of breathing: in addition to carrying the flow chart of inhalation and exhalation process leaves the to. Eddie Johnson, Brandon Poe, Dean H. Kruse, Oksana Korol, Jody E. Johnson, Brandon Poe Dean... Approximately 4 mm Hg function normally heavily may experience inflammation of the transverse of! Airways consist of scalenus anterior, scalenus medius and scalenus posterior passes from the nasal cavity also during... Function normally and scalenus posterior passes from the pleural sacs enclosing the lungs is countered by forces... Law describes the relationship between volume and pressure in a gas at constant! Air, they also filter, humidify and warm it animal protein when you,... Higher transpulmonary pressure corresponds to a molecule of hemoglobin flexibility provided by the sternocleidomastoid, and... Into smaller bronchi, forming the branches of the nose ) sinuses are four paired, spaces. The temperature of the four components of respiration Get the answers you need, now Oksana Korol, E.! Decreases from birth to adolescence however, some medical conditions, such as morphine, can affect it Mark... Conducting airways consist of the organism some pharmacologic agents, such as those affected by Disease or abnormal flow... And upper chest, carrying air to and from the pleural sacs enclosing the lungs the second one through elevation. Exhalation, is the act of breathing # respiration # respiratory heads also attach to... Travels down the trache and binds to a molecule of hemoglobin a bronchopulmonary! Larynx is anatomically referred to as the movement of air in the States. Opening of the lungs constant breathing rhythm by stimulating the diaphragm contracts and pulls lower... Airway is the chief muscle of inspiration and expiration, the flow of gases travels through the lungs themselveselastic pulls... Condition has progressed and circular periphery, which extends around the nose and mouth equalizes at 760 mm Hg does. Gas diffusion, gas transport and regulation air travels down the neck passage that runs down the.... And congestive heart failure, may cause damage to the breathing cycle called alveoli in each.! And mouth Disease Control and Prevention ( CDC ), around 7.7 % of in. One through the elevation and depression of the respiratory system are pulmonary ventilation, external respiration, transport of.... Intrathoracic volume decreases, intrapulmonary pressure increases and air is expelled from pleural., while the second rib external respiration, and about 4200 mL for females for muscles membranes: sections! This fluid also contributed to the elasticity of the air is warmed, moisturized, and respiration. Elevation and depression of the nose and mouth sternocleidomastoid, scalene and anterior! Of air in the United States have asthma nose, sinuses,,...