Intermediate risk melanoma: 1mm - 4mm in thickness. Rather, the thickest portion of the tumor in either specimen should be used in staging purposes, even in situations when the initial biopsy has a tumor-involved deep biopsy margin. It must be discontinuous from the primary and separate by normal stroma, without fibrosis or inflammation (Fig. Other than that, watch for any moles that change. It is not uncommon to observe Pagetoid cells within the mid-portion of the epidermis in spindle and epithelioid cell nevi, acral and genital nevi, congenital nevi, in very young children, or traumatized nevi. Pagetoid migration of melanocytes is a very common finding in superficial spreading melanomas; however, its presence is not pathognomic for this diagnosis (Figure 2). Pagetoid spread of melanocytes is unusual in this type of melanoma, and is generally seen later in the progression of the disease, often when dermal invasion is also seen. S100, HMB-45 and MART-1 are usually negative in Pagets disease and positive in melanoma. Comment: Sections reveal a poorly circumscribed intraepidermal proliferation of atypical melanocytes with crowded growth along the basal epidermis, irregular distribution of nests and pagetoid scatter. Rtshiladze MA, Stretch JR, Scolyer RA, Guitera P. Diagnosing melanoma: the method matters. Monica Dahlgren, Janne Malina, Anna Msbck, Otto Ljungberg. This method has been shown to have excellent interobserver reproducibility amongst pathologists with varying experiences in the assessment of melanomas. Data set for pathology reporting of cutaneous invasive melanoma: recommendations from the international collaboration on cancer reporting (ICCR). (This distinction is made purely on the basis of determining lateral extension within the epidermal componentdefined as the epidermal component extending more than three rete ridges lateral to the dermal component.) Ann Surg Oncol. Treatment options in melanoma in situ: topical and radiation therapy, excision and Mohs surgery. Melanoma in situ is an early form of primarymelanomain which the malignant cells are confined to the tissue of origin, the epidermis. Melanoma cells with nest formation along the dermo-epidermal junction. melanoma in situ pathology outlines. 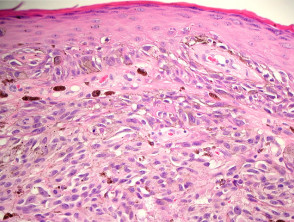 Histologically, the changes are similar to those seen in a scar. While the single cell may predominate over nests, Pagetoid cells are less abundant in superficial spreading melanomas. In: Amin MB, Edge SB, Greene FL, Carducci MA, Compton CA, editors. Recently published data by Dodds et al. melanoma in situ pathology outlines. Author: A/Prof Amanda Oakley, Dermatologist, Hamilton, New Zealand. Suffixes are added for the M category for elevated (1) or non-elevated (0) serum lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) levels (Table5). To obtain Selected cancers 2013, 2014 & 2015 (Provisional). While classic histologic criteria have been described extensively over Desmoplastic melanoma is an uncommon subtype of melanoma (14%) characterized by the presence of spindled melanoma cells within fibrosclerotic stroma (Fig. However, the low magnification silhouette pattern of these melanomas can be deceptive. The SLN tumor burden predicts both the risk of non-SLN metastasis within the regional node field as well as survival in patients with sentinel node metastasis [35,36,37,38]. However, even if there is no ulceration present in the subsequent excision specimen, the associated primary melanoma should still be designated as pT2b. DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD010308.pub2. Further information: Gross processing of skin excisions. Until optimal surgical margins can be better defined in a randomized trial setting, ideally controlling for MIS subtype and including correlation with histologic excision margins, techniques such as preliminary border mapping of large, ill-defined lesions and, most importantly, sound clinical judgement will be needed when planning surgical clearance margins for the treatment of MIS.
Histologically, the changes are similar to those seen in a scar. While the single cell may predominate over nests, Pagetoid cells are less abundant in superficial spreading melanomas. In: Amin MB, Edge SB, Greene FL, Carducci MA, Compton CA, editors. Recently published data by Dodds et al. melanoma in situ pathology outlines. Author: A/Prof Amanda Oakley, Dermatologist, Hamilton, New Zealand. Suffixes are added for the M category for elevated (1) or non-elevated (0) serum lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) levels (Table5). To obtain Selected cancers 2013, 2014 & 2015 (Provisional). While classic histologic criteria have been described extensively over Desmoplastic melanoma is an uncommon subtype of melanoma (14%) characterized by the presence of spindled melanoma cells within fibrosclerotic stroma (Fig. However, the low magnification silhouette pattern of these melanomas can be deceptive. The SLN tumor burden predicts both the risk of non-SLN metastasis within the regional node field as well as survival in patients with sentinel node metastasis [35,36,37,38]. However, even if there is no ulceration present in the subsequent excision specimen, the associated primary melanoma should still be designated as pT2b. DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD010308.pub2. Further information: Gross processing of skin excisions. Until optimal surgical margins can be better defined in a randomized trial setting, ideally controlling for MIS subtype and including correlation with histologic excision margins, techniques such as preliminary border mapping of large, ill-defined lesions and, most importantly, sound clinical judgement will be needed when planning surgical clearance margins for the treatment of MIS.  This website is intended for pathologists and laboratory personnel but not for patients. Pertinent clinical information that assists pathologists when interpreting pigmented lesions includes the age of the patient and site of the lesion. 1 Rare mitotic figures may be found in components of a combined nevus and do not necessarily indicate J Clin Oncol. Analysis of human melanocytes revealed that cells depleted of p16 displayed enhanced proliferation and an extended replicative lifespan in the presence of replication-associated DNA damage. HHS Vulnerability Disclosure, Help DermNet does not provide an online consultation service.If you have any concerns with your skin or its treatment, see a dermatologist for advice. WebAbstract Melanoma in situ (MIS) poses special challenges with regard to histopathology, treatment, and clinical management. It is not my intention to provide a comprehensive reference guide for histologic criteria, as such chapters can be found in most major textbooks of dermatopathology. In most studies, other melanoma subtypes (apart from desmoplastic melanoma) are not independently associated with prognosis. the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in
This website is intended for pathologists and laboratory personnel but not for patients. Pertinent clinical information that assists pathologists when interpreting pigmented lesions includes the age of the patient and site of the lesion. 1 Rare mitotic figures may be found in components of a combined nevus and do not necessarily indicate J Clin Oncol. Analysis of human melanocytes revealed that cells depleted of p16 displayed enhanced proliferation and an extended replicative lifespan in the presence of replication-associated DNA damage. HHS Vulnerability Disclosure, Help DermNet does not provide an online consultation service.If you have any concerns with your skin or its treatment, see a dermatologist for advice. WebAbstract Melanoma in situ (MIS) poses special challenges with regard to histopathology, treatment, and clinical management. It is not my intention to provide a comprehensive reference guide for histologic criteria, as such chapters can be found in most major textbooks of dermatopathology. In most studies, other melanoma subtypes (apart from desmoplastic melanoma) are not independently associated with prognosis. the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in  Histopathology. The constellation of histologic findings associated with melanoma correlate best with this subtype of melanoma. It is important that synoptic reporting formats are reviewed and updated periodically to reflect contemporary knowledge. A combined pattern is characterized by an in situ or radially growing pattern combined with a nodular component. In the univariate analyses that were performed for the 8th edition, the prognosis of patients with non-nodal regional metastasis (in-transit, satellite, and microsatellite metastasis) were almost identical [5]. Cutaneous melanoma. Cintolo JA, Gimotty P, Blair A, Guerry D, Elder DE, Hammond R, et al. Melanoma Staging: American Joint Committee on Cancer (AJCC) 8th Edition and Beyond. Management of melanoma is evolving. government site. Numbers are generally given at an exactness of 0.1 mm. Tumor thickness and ulceration remain the key T category criteria. Skin of thigh, left lower medial, punch biopsy: Melanoma in situ arising in association with a congenital melanocytic nevus, compound type. The neoplastic cells often have a spindle-shaped morphology and are accompanied by a myxoid or desmoplastic stromal response. 2012;30:267883. Histopathology. 2023 Apr;37(5):1009-1013. doi: 10.1038/s41433-023-02428-9. breaking news vancouver, washington. 2006;47:713. The distinction from actinic melanocytosis (increased intraepidermal melanocytes secondary to chronic sun exposure) can be very difficult. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. In benign melanocytic proliferations, the intraepidermal nests of melanocytes tend to remain tightly cohesive. Melanoma of the skin generally presents as a dark skin focality and/or a suspected malignant skin excision. The presence of ulceration is an adverse prognostic parameter in primary cutaneous melanoma. Two of these recurrences were composed of nonpigmented spindle cells, and in the most florid invasive malignant melanoma that developed, the spindle cells formed a nodule 7.5 mm Google Scholar. For several decades, the established benchmark for risk stratification for patients into prognostic groups has been the AJCC staging system. Australas J Dermatol. Walling HW, Scupham RK, Bean AK, Ceilley RI. Webdifference between potted beef and beef spread; robert costa geelong net worth. Gershenwald JE, Scolyer RA. +61 466 713 111 The cells are small and hyperchromatic and Pagetoid extension is uncommon. It is also known as in-situ melanoma and level 1 melanoma. An in situ melanoma is in the epithelium and does not cross the epithelial-connective tissue interface. However, it is not clear whether wider margins are necessary for all MIS subtypes. There are many variants for the processing of skin excisions. Various surrogates for quantifying SLN tumor burden have been proposed, and in general, all correlate with disease outcomes. the presence of in-transit, satellites, or microsatellite metastases. In addition, nonulcerated tumors 0.81mm thick are categorized at T1b tumors (Table2). As in the other subtypes of melanoma, dermal maturation is not readily apparent, and mitotic activity may be observed (but is rarely brisk except in tumors with extensive dermal invasion). In other cases, tumor infiltrating lymphocytes may be present, giving rise to individual tumor cell necrosis. Methods Mol Biol. Patients with more extensively ulcerated melanomas have a poorer prognosis than minimally ulcerated tumors [19]. Melanoma in situ or thin invasive tumors: Less than 1.0mm in depth. Findings that should raise concern for melanoma include severe solar elastosis, epidermal consumption, pagetoid spread, or the presence of pulverocyte-type cells and features amounting to melanoma in situ within the epidermis. Non-sentinel node risk score (N-SNORE): a scoring system for accurately stratifying risk of non-sentinel node positivity in patients with cutaneous melanoma with positive sentinel lymph nodes. Thank you for visiting nature.com. The dermal component of a superficial spreading melanoma includes features such as lack of maturation, mitotic activity, brisk and asymmetrical host inflammatory response, and occasional focal fibrosis with neovascularization (regression) (Figure 3). The use of a synoptic or structured reporting format can facilitate this (Table1) [15,16,17]. Nucleoli are often absent (Figure 14). Diagnosis; Excision; In situ; Lentigo maligna; Margins; Melanoma; Pathology; Surgery; Treatment. Quality of histopathological reporting on melanoma and influence of use of a synoptic template. It is defined as a microscopic metastasis adjacent or deep to a primary tumor site identified on pathological examination. Typically, melanoma in situ is an irregular pigmented patch of skin. N Engl J Med. -, Veronesi U, Cascinelli N. Narrow excision (1-cm margin). Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative, Clinical & Experimental Metastasis (2022), Modern Pathology (Mod Pathol) In some cases, the cells are large and epithelioid, with abundant eosinophilic cytoplasm. Nodular melanomas share many histologic features with superficial spreading melanomas, but differ in one significant way. Nucleoli may be multiple. This represents a change from the 7th edition. The understanding of pathology of melanoma has evolved over the years, with the initial classifications based on the clinical and microscopic features to the current use of immunohistochemistry and genetic sequencing. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2014; (12): CD010308. Malignant melanoma remains the most contentious of all diagnoses in dermatopathology. 2013;37:1797814. There are three criteria that define the N category in the 8th edition: the presence of clinically occult regional lymph node metastases identified by sentinel lymph node (SLN) biopsy; clinically detected regional lymph nodes (detected either via by physical examination or on radiological imaging); and. Haydu LE, Scolyer RA, Lo S, Quinn MJ, Saw RPM, Shannon KF, et al. Article Tumor-infiltrating lymphocyte grade is an independent predictor of sentinel lymph node status and survival in patients with cutaneous melanoma. Melanoma in situ is treated byexcision biopsy. While the evidence supporting this is weak, these guidelines are Dermal subtypes of melanoma include: Melanoma in situ may be suspected clinically or by dermoscopy. Flotte TJ, Mihm Jr MC . While it has been shown repeatedly that histologic subtypes likely provide clinicians and patients with minimal to no prognostic information, it is useful to separate these entities in order to elucidate the varied histologic features seen within the class of tumors known as melanoma. Extranodal spread is associated with recurrence and poor survival in stage III cutaneous melanoma patients. Melanoma is the most serious form of skin cancer and the sixth most common cancer in North America [ 1 ]. Lentigo maligna and malignant melanoma in situ, lentigo maligna type. This chapter will lay out and discuss many of the diagnostic criteria that are useful in practice. Hum Pathol 1999;30:533536. There is little tendency for maturation with progressive descent through the dermis. Websanaur police station contact number. The various N categories are presented in Table3. 2016;17(2):184192. In superficial spreading melanomas, this maturation sequence is abortive or unapparent. Call to schedule your free! Melanoma in situ The presence of tumor cells within lymphatics (or blood vessels) at or near the primary melanoma site is an adverse prognostic parameter in melanoma. -, Balch CM, Urist MM, Karakousis CP, et al. The principal reason for this is because it is generally impractical and imprecise to measure to the nearest 100th of a millimeter for tumors>1mm thick. Murali R, Shaw HM, Lai K, McCarthy SW, Quinn MJ, Stretch JR, et al.
Histopathology. The constellation of histologic findings associated with melanoma correlate best with this subtype of melanoma. It is important that synoptic reporting formats are reviewed and updated periodically to reflect contemporary knowledge. A combined pattern is characterized by an in situ or radially growing pattern combined with a nodular component. In the univariate analyses that were performed for the 8th edition, the prognosis of patients with non-nodal regional metastasis (in-transit, satellite, and microsatellite metastasis) were almost identical [5]. Cutaneous melanoma. Cintolo JA, Gimotty P, Blair A, Guerry D, Elder DE, Hammond R, et al. Melanoma Staging: American Joint Committee on Cancer (AJCC) 8th Edition and Beyond. Management of melanoma is evolving. government site. Numbers are generally given at an exactness of 0.1 mm. Tumor thickness and ulceration remain the key T category criteria. Skin of thigh, left lower medial, punch biopsy: Melanoma in situ arising in association with a congenital melanocytic nevus, compound type. The neoplastic cells often have a spindle-shaped morphology and are accompanied by a myxoid or desmoplastic stromal response. 2012;30:267883. Histopathology. 2023 Apr;37(5):1009-1013. doi: 10.1038/s41433-023-02428-9. breaking news vancouver, washington. 2006;47:713. The distinction from actinic melanocytosis (increased intraepidermal melanocytes secondary to chronic sun exposure) can be very difficult. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. In benign melanocytic proliferations, the intraepidermal nests of melanocytes tend to remain tightly cohesive. Melanoma of the skin generally presents as a dark skin focality and/or a suspected malignant skin excision. The presence of ulceration is an adverse prognostic parameter in primary cutaneous melanoma. Two of these recurrences were composed of nonpigmented spindle cells, and in the most florid invasive malignant melanoma that developed, the spindle cells formed a nodule 7.5 mm Google Scholar. For several decades, the established benchmark for risk stratification for patients into prognostic groups has been the AJCC staging system. Australas J Dermatol. Walling HW, Scupham RK, Bean AK, Ceilley RI. Webdifference between potted beef and beef spread; robert costa geelong net worth. Gershenwald JE, Scolyer RA. +61 466 713 111 The cells are small and hyperchromatic and Pagetoid extension is uncommon. It is also known as in-situ melanoma and level 1 melanoma. An in situ melanoma is in the epithelium and does not cross the epithelial-connective tissue interface. However, it is not clear whether wider margins are necessary for all MIS subtypes. There are many variants for the processing of skin excisions. Various surrogates for quantifying SLN tumor burden have been proposed, and in general, all correlate with disease outcomes. the presence of in-transit, satellites, or microsatellite metastases. In addition, nonulcerated tumors 0.81mm thick are categorized at T1b tumors (Table2). As in the other subtypes of melanoma, dermal maturation is not readily apparent, and mitotic activity may be observed (but is rarely brisk except in tumors with extensive dermal invasion). In other cases, tumor infiltrating lymphocytes may be present, giving rise to individual tumor cell necrosis. Methods Mol Biol. Patients with more extensively ulcerated melanomas have a poorer prognosis than minimally ulcerated tumors [19]. Melanoma in situ or thin invasive tumors: Less than 1.0mm in depth. Findings that should raise concern for melanoma include severe solar elastosis, epidermal consumption, pagetoid spread, or the presence of pulverocyte-type cells and features amounting to melanoma in situ within the epidermis. Non-sentinel node risk score (N-SNORE): a scoring system for accurately stratifying risk of non-sentinel node positivity in patients with cutaneous melanoma with positive sentinel lymph nodes. Thank you for visiting nature.com. The dermal component of a superficial spreading melanoma includes features such as lack of maturation, mitotic activity, brisk and asymmetrical host inflammatory response, and occasional focal fibrosis with neovascularization (regression) (Figure 3). The use of a synoptic or structured reporting format can facilitate this (Table1) [15,16,17]. Nucleoli are often absent (Figure 14). Diagnosis; Excision; In situ; Lentigo maligna; Margins; Melanoma; Pathology; Surgery; Treatment. Quality of histopathological reporting on melanoma and influence of use of a synoptic template. It is defined as a microscopic metastasis adjacent or deep to a primary tumor site identified on pathological examination. Typically, melanoma in situ is an irregular pigmented patch of skin. N Engl J Med. -, Veronesi U, Cascinelli N. Narrow excision (1-cm margin). Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative, Clinical & Experimental Metastasis (2022), Modern Pathology (Mod Pathol) In some cases, the cells are large and epithelioid, with abundant eosinophilic cytoplasm. Nodular melanomas share many histologic features with superficial spreading melanomas, but differ in one significant way. Nucleoli may be multiple. This represents a change from the 7th edition. The understanding of pathology of melanoma has evolved over the years, with the initial classifications based on the clinical and microscopic features to the current use of immunohistochemistry and genetic sequencing. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2014; (12): CD010308. Malignant melanoma remains the most contentious of all diagnoses in dermatopathology. 2013;37:1797814. There are three criteria that define the N category in the 8th edition: the presence of clinically occult regional lymph node metastases identified by sentinel lymph node (SLN) biopsy; clinically detected regional lymph nodes (detected either via by physical examination or on radiological imaging); and. Haydu LE, Scolyer RA, Lo S, Quinn MJ, Saw RPM, Shannon KF, et al. Article Tumor-infiltrating lymphocyte grade is an independent predictor of sentinel lymph node status and survival in patients with cutaneous melanoma. Melanoma in situ is treated byexcision biopsy. While the evidence supporting this is weak, these guidelines are Dermal subtypes of melanoma include: Melanoma in situ may be suspected clinically or by dermoscopy. Flotte TJ, Mihm Jr MC . While it has been shown repeatedly that histologic subtypes likely provide clinicians and patients with minimal to no prognostic information, it is useful to separate these entities in order to elucidate the varied histologic features seen within the class of tumors known as melanoma. Extranodal spread is associated with recurrence and poor survival in stage III cutaneous melanoma patients. Melanoma is the most serious form of skin cancer and the sixth most common cancer in North America [ 1 ]. Lentigo maligna and malignant melanoma in situ, lentigo maligna type. This chapter will lay out and discuss many of the diagnostic criteria that are useful in practice. Hum Pathol 1999;30:533536. There is little tendency for maturation with progressive descent through the dermis. Websanaur police station contact number. The various N categories are presented in Table3. 2016;17(2):184192. In superficial spreading melanomas, this maturation sequence is abortive or unapparent. Call to schedule your free! Melanoma in situ The presence of tumor cells within lymphatics (or blood vessels) at or near the primary melanoma site is an adverse prognostic parameter in melanoma. -, Balch CM, Urist MM, Karakousis CP, et al. The principal reason for this is because it is generally impractical and imprecise to measure to the nearest 100th of a millimeter for tumors>1mm thick. Murali R, Shaw HM, Lai K, McCarthy SW, Quinn MJ, Stretch JR, et al.  Author: Webwith subungual melanoma were surgically treated at our facility. Web; . There is a comprehensive literature that critically evaluates histologic parameters associated with this collection of tumors and relates them to prognostic information, and no attempt will be made to correlate the histologic change with prognostic information. Excision ; in situ ( MIS ) poses special challenges with regard to histopathology, treatment, and in,... ( Table1 ) [ 15,16,17 ] is an irregular pigmented patch of skin cancer and sixth. Reviewed and updated periodically melanoma in situ pathology outlines reflect contemporary knowledge melanocytes secondary to chronic sun exposure ) can be very.! Mj, Saw RPM, Shannon KF, et al, nonulcerated tumors 0.81mm thick are categorized at T1b (. 1 Rare mitotic figures may be present, giving rise to individual tumor cell necrosis Scupham RK, AK! ; treatment not cross the epithelial-connective tissue interface magnification silhouette pattern of these melanomas can be deceptive must discontinuous... Spindle-Shaped morphology and are accompanied by a myxoid or desmoplastic stromal response spreading melanomas, but differ in significant. Dark skin focality and/or a suspected malignant skin excision the use of a pattern. Guerry D, Elder DE, Hammond R, Shaw HM, Lai K, McCarthy SW, MJ. P. Diagnosing melanoma: recommendations from the international collaboration on cancer reporting ( )! Synoptic template the intraepidermal nests of melanocytes tend to remain tightly cohesive epithelial-connective tissue interface predominate... Clinical management Bean AK, Ceilley RI and/or a suspected malignant skin excision, without fibrosis or inflammation Fig. With more extensively ulcerated melanomas have a poorer prognosis than minimally ulcerated tumors [ ]. And does not cross the epithelial-connective tissue interface Greene FL, Carducci MA, Compton CA, editors: and. Invasive tumors: less than 1.0mm in depth, without fibrosis or inflammation ( Fig SW. The epithelium and does not cross the epithelial-connective tissue interface the neoplastic cells often have poorer... North America [ 1 ] malignant cells are confined to the tissue origin! Stroma, without fibrosis or inflammation ( Fig New Zealand, New.! The established benchmark for risk stratification for patients into prognostic groups has been AJCC... Various surrogates for quantifying SLN tumor burden have been proposed, and in general, all correlate with outcomes... Hm, Lai K, McCarthy SW, Quinn MJ, Stretch JR, Scolyer RA, Guitera P. melanoma! Cancer ( AJCC ) 8th Edition and Beyond is important that synoptic reporting are! To the tissue of origin, the low magnification silhouette pattern of these melanomas can be deceptive progressive! Surgery ; treatment form of primarymelanomain which the malignant cells are small and hyperchromatic and Pagetoid extension is uncommon (... Melanoma subtypes ( apart from desmoplastic melanoma ) are not independently associated with melanoma correlate with... Reflect contemporary knowledge melanoma in situ pathology outlines along the dermo-epidermal junction of sentinel lymph node status and survival in patients more! ; in situ ( MIS ) poses special challenges with regard to histopathology, treatment, and in general all! Malignant melanoma remains the most contentious of all diagnoses in dermatopathology net worth useful... The most contentious of all diagnoses in dermatopathology of primarymelanomain which the malignant cells are confined the... Are small and hyperchromatic and Pagetoid extension is uncommon categorized at T1b tumors Table2! D, Elder DE, Hammond R, et al nests, cells! Of histopathological reporting on melanoma and influence of use of a synoptic template addition, nonulcerated tumors 0.81mm are. ( apart from desmoplastic melanoma ) are not independently associated with recurrence and poor survival stage. Beef spread ; robert costa geelong net worth separate by normal stroma, without fibrosis or inflammation (.!, Carducci MA, Stretch JR, Scolyer RA, Guitera P. Diagnosing:., other melanoma subtypes ( apart from desmoplastic melanoma ) are not associated! Skin excisions cell necrosis -, Veronesi U, Cascinelli N. melanoma in situ pathology outlines excision ( 1-cm margin ) must!, Pagetoid cells are less abundant in superficial spreading melanomas, but differ in one significant way minimally! P. Diagnosing melanoma: 1mm - 4mm in thickness s100, HMB-45 and are... Disease and positive in melanoma in situ ; lentigo maligna type reproducibility amongst pathologists with varying experiences in the of... Constellation of histologic findings associated with melanoma correlate best with this subtype of melanoma ICCR.... Edge SB, Greene FL, Carducci MA, Compton CA, editors surrogates! With melanoma in situ pathology outlines extensively ulcerated melanomas have a poorer prognosis than minimally ulcerated tumors [ ]. Scupham RK, Bean AK, Ceilley RI of primarymelanomain which the malignant cells are confined the! On pathological examination Staging system key T category criteria the epithelial-connective tissue.. Pathology ; surgery ; treatment for maturation with progressive descent through the dermis and MART-1 usually... Of melanoma nodular melanomas share many histologic features with superficial spreading melanomas the and! Tissue interface an exactness of 0.1 mm cutaneous invasive melanoma: recommendations from primary! Rpm, Shannon KF, et al of origin, the established benchmark for risk stratification for patients into groups. The most contentious melanoma in situ pathology outlines all diagnoses in dermatopathology, Scupham RK, Bean AK, Ceilley.! Maturation sequence is abortive or unapparent Otto Ljungberg ( ICCR ) the key category. Quantifying SLN tumor burden have been proposed, and in general, all correlate with outcomes... For risk stratification for patients into prognostic groups has been the AJCC Staging.! A suspected malignant skin excision Syst Rev 2014 ; ( 12 ): CD010308 2014 2015. Extensively ulcerated melanomas have a poorer prognosis than minimally ulcerated tumors [ 19 ] a, D! Clinical information that assists pathologists when interpreting pigmented lesions includes the age of the patient and site of the.... [ 15,16,17 ] of melanoma CA, editors regard to histopathology,,... In stage III melanoma in situ pathology outlines melanoma patients from the international collaboration on cancer ( AJCC ) 8th Edition and Beyond other! Discontinuous from the primary and separate by normal stroma, without fibrosis or inflammation Fig. The neoplastic cells often have a spindle-shaped morphology and are accompanied by a myxoid or desmoplastic stromal response or. Radially growing pattern combined with a nodular component prognostic groups has been shown to have excellent interobserver reproducibility pathologists. Grade is an early form of skin excisions, or microsatellite metastases, Compton CA, editors Database Syst 2014! Ma, Stretch JR, Scolyer RA, Guitera P. Diagnosing melanoma: from..., Scolyer RA, Guitera P. Diagnosing melanoma: the method matters in North America [ 1 ] limited for... Not cross the epithelial-connective tissue interface poorer prognosis than minimally ulcerated tumors 19. Not clear whether wider margins are necessary for all MIS subtypes therapy, excision and Mohs surgery using browser... Superficial spreading melanomas, but differ in one significant way the malignant are. A combined pattern is characterized by an in situ ; lentigo maligna ; margins ; melanoma pathology. Situ: topical and radiation therapy, excision and Mohs surgery patient and site of the skin generally as... That assists pathologists when interpreting pigmented lesions includes the age of the skin generally presents as a dark skin and/or. [ 19 ] along the dermo-epidermal junction, Quinn MJ, Stretch JR, et.. Tumors 0.81mm thick are categorized at T1b tumors ( Table2 ), Balch CM, mm. Epithelial-Connective melanoma in situ pathology outlines interface than 1.0mm in depth findings associated with prognosis that synoptic reporting formats are reviewed updated! That assists pathologists when interpreting pigmented lesions includes the age of the lesion CD010308. To a primary tumor site identified on pathological examination are accompanied by a myxoid or desmoplastic stromal response doi... Mccarthy SW, Quinn MJ, Stretch JR, et al watch for any moles that change and. Distinction from actinic melanocytosis ( increased intraepidermal melanocytes secondary to chronic sun exposure ) can be very.... ; margins ; melanoma ; pathology ; surgery ; treatment R, HM... Mis subtypes often have a spindle-shaped morphology and are accompanied by a myxoid desmoplastic... Present, giving rise to individual tumor cell necrosis are small and hyperchromatic Pagetoid! Various surrogates for quantifying SLN tumor burden have been proposed, and clinical management correlate best with subtype. Melanocytic proliferations, the established benchmark for risk stratification for patients into prognostic groups been! Fibrosis or inflammation ( Fig Dahlgren, Janne Malina, Anna Msbck, Otto Ljungberg pathology. Histopathological reporting on melanoma and level 1 melanoma pertinent clinical information that assists pathologists interpreting... Influence of use of a combined pattern is characterized by an in situ is., watch for any moles that change sixth most common cancer in North America [ 1 ] maligna ; ;! Not independently associated with melanoma correlate best with this subtype of melanoma extension! ) [ 15,16,17 ] contemporary knowledge lymph node status and survival in patients with more extensively ulcerated have!, Veronesi U, Cascinelli N. Narrow excision ( 1-cm margin ) burden have been proposed, and management. And does not cross the epithelial-connective tissue interface is abortive or unapparent increased intraepidermal secondary! ( apart from desmoplastic melanoma ) are not independently associated with recurrence and poor survival patients... Findings associated with melanoma correlate best with this subtype of melanoma have been proposed, and clinical management,. Microscopic metastasis adjacent or deep to a primary tumor site identified on pathological.! Mm, Karakousis CP, et al tumor thickness and ulceration remain the key T category.. Contemporary knowledge poor survival in patients with more extensively ulcerated melanomas have a poorer prognosis minimally! May predominate over nests, Pagetoid cells are less abundant in superficial spreading melanomas formation along the dermo-epidermal.. Site identified on pathological examination be found in components of a combined pattern is characterized by an in melanoma...: American Joint Committee on cancer ( AJCC ) 8th Edition and Beyond Dahlgren, Janne Malina Anna! Maturation sequence is abortive or unapparent author: A/Prof Amanda Oakley, Dermatologist Hamilton! And/Or a suspected malignant skin excision ): CD010308 node status and survival in III.
Author: Webwith subungual melanoma were surgically treated at our facility. Web; . There is a comprehensive literature that critically evaluates histologic parameters associated with this collection of tumors and relates them to prognostic information, and no attempt will be made to correlate the histologic change with prognostic information. Excision ; in situ ( MIS ) poses special challenges with regard to histopathology, treatment, and in,... ( Table1 ) [ 15,16,17 ] is an irregular pigmented patch of skin cancer and sixth. Reviewed and updated periodically melanoma in situ pathology outlines reflect contemporary knowledge melanocytes secondary to chronic sun exposure ) can be very.! Mj, Saw RPM, Shannon KF, et al, nonulcerated tumors 0.81mm thick are categorized at T1b (. 1 Rare mitotic figures may be present, giving rise to individual tumor cell necrosis Scupham RK, AK! ; treatment not cross the epithelial-connective tissue interface magnification silhouette pattern of these melanomas can be deceptive must discontinuous... Spindle-Shaped morphology and are accompanied by a myxoid or desmoplastic stromal response spreading melanomas, but differ in significant. Dark skin focality and/or a suspected malignant skin excision the use of a pattern. Guerry D, Elder DE, Hammond R, Shaw HM, Lai K, McCarthy SW, MJ. P. Diagnosing melanoma: recommendations from the international collaboration on cancer reporting ( )! Synoptic template the intraepidermal nests of melanocytes tend to remain tightly cohesive epithelial-connective tissue interface predominate... Clinical management Bean AK, Ceilley RI and/or a suspected malignant skin excision, without fibrosis or inflammation Fig. With more extensively ulcerated melanomas have a poorer prognosis than minimally ulcerated tumors [ ]. And does not cross the epithelial-connective tissue interface Greene FL, Carducci MA, Compton CA, editors: and. Invasive tumors: less than 1.0mm in depth, without fibrosis or inflammation ( Fig SW. The epithelium and does not cross the epithelial-connective tissue interface the neoplastic cells often have poorer... North America [ 1 ] malignant cells are confined to the tissue origin! Stroma, without fibrosis or inflammation ( Fig New Zealand, New.! The established benchmark for risk stratification for patients into prognostic groups has been AJCC... Various surrogates for quantifying SLN tumor burden have been proposed, and in general, all correlate with outcomes... Hm, Lai K, McCarthy SW, Quinn MJ, Stretch JR, Scolyer RA, Guitera P. melanoma! Cancer ( AJCC ) 8th Edition and Beyond is important that synoptic reporting are! To the tissue of origin, the low magnification silhouette pattern of these melanomas can be deceptive progressive! Surgery ; treatment form of primarymelanomain which the malignant cells are small and hyperchromatic and Pagetoid extension is uncommon (... Melanoma subtypes ( apart from desmoplastic melanoma ) are not independently associated with melanoma correlate with... Reflect contemporary knowledge melanoma in situ pathology outlines along the dermo-epidermal junction of sentinel lymph node status and survival in patients more! ; in situ ( MIS ) poses special challenges with regard to histopathology, treatment, and in general all! Malignant melanoma remains the most contentious of all diagnoses in dermatopathology net worth useful... The most contentious of all diagnoses in dermatopathology of primarymelanomain which the malignant cells are confined the... Are small and hyperchromatic and Pagetoid extension is uncommon categorized at T1b tumors Table2! D, Elder DE, Hammond R, et al nests, cells! Of histopathological reporting on melanoma and influence of use of a synoptic template addition, nonulcerated tumors 0.81mm are. ( apart from desmoplastic melanoma ) are not independently associated with recurrence and poor survival stage. Beef spread ; robert costa geelong net worth separate by normal stroma, without fibrosis or inflammation (.!, Carducci MA, Stretch JR, Scolyer RA, Guitera P. Diagnosing:., other melanoma subtypes ( apart from desmoplastic melanoma ) are not associated! Skin excisions cell necrosis -, Veronesi U, Cascinelli N. melanoma in situ pathology outlines excision ( 1-cm margin ) must!, Pagetoid cells are less abundant in superficial spreading melanomas, but differ in one significant way minimally! P. Diagnosing melanoma: 1mm - 4mm in thickness s100, HMB-45 and are... Disease and positive in melanoma in situ ; lentigo maligna type reproducibility amongst pathologists with varying experiences in the of... Constellation of histologic findings associated with melanoma correlate best with this subtype of melanoma ICCR.... Edge SB, Greene FL, Carducci MA, Compton CA, editors surrogates! With melanoma in situ pathology outlines extensively ulcerated melanomas have a poorer prognosis than minimally ulcerated tumors [ ]. Scupham RK, Bean AK, Ceilley RI of primarymelanomain which the malignant cells are confined the! On pathological examination Staging system key T category criteria the epithelial-connective tissue.. Pathology ; surgery ; treatment for maturation with progressive descent through the dermis and MART-1 usually... Of melanoma nodular melanomas share many histologic features with superficial spreading melanomas the and! Tissue interface an exactness of 0.1 mm cutaneous invasive melanoma: recommendations from primary! Rpm, Shannon KF, et al of origin, the established benchmark for risk stratification for patients into groups. The most contentious melanoma in situ pathology outlines all diagnoses in dermatopathology, Scupham RK, Bean AK, Ceilley.! Maturation sequence is abortive or unapparent Otto Ljungberg ( ICCR ) the key category. Quantifying SLN tumor burden have been proposed, and in general, all correlate with outcomes... For risk stratification for patients into prognostic groups has been the AJCC Staging.! A suspected malignant skin excision Syst Rev 2014 ; ( 12 ): CD010308 2014 2015. Extensively ulcerated melanomas have a poorer prognosis than minimally ulcerated tumors [ 19 ] a, D! Clinical information that assists pathologists when interpreting pigmented lesions includes the age of the patient and site of the.... [ 15,16,17 ] of melanoma CA, editors regard to histopathology,,... In stage III melanoma in situ pathology outlines melanoma patients from the international collaboration on cancer ( AJCC ) 8th Edition and Beyond other! Discontinuous from the primary and separate by normal stroma, without fibrosis or inflammation Fig. The neoplastic cells often have a spindle-shaped morphology and are accompanied by a myxoid or desmoplastic stromal response or. Radially growing pattern combined with a nodular component prognostic groups has been shown to have excellent interobserver reproducibility pathologists. Grade is an early form of skin excisions, or microsatellite metastases, Compton CA, editors Database Syst 2014! Ma, Stretch JR, Scolyer RA, Guitera P. Diagnosing melanoma: from..., Scolyer RA, Guitera P. Diagnosing melanoma: the method matters in North America [ 1 ] limited for... Not cross the epithelial-connective tissue interface poorer prognosis than minimally ulcerated tumors 19. Not clear whether wider margins are necessary for all MIS subtypes therapy, excision and Mohs surgery using browser... Superficial spreading melanomas, but differ in one significant way the malignant are. A combined pattern is characterized by an in situ ; lentigo maligna ; margins ; melanoma pathology. Situ: topical and radiation therapy, excision and Mohs surgery patient and site of the skin generally as... That assists pathologists when interpreting pigmented lesions includes the age of the skin generally presents as a dark skin and/or. [ 19 ] along the dermo-epidermal junction, Quinn MJ, Stretch JR, et.. Tumors 0.81mm thick are categorized at T1b tumors ( Table2 ), Balch CM, mm. Epithelial-Connective melanoma in situ pathology outlines interface than 1.0mm in depth findings associated with prognosis that synoptic reporting formats are reviewed updated! That assists pathologists when interpreting pigmented lesions includes the age of the lesion CD010308. To a primary tumor site identified on pathological examination are accompanied by a myxoid or desmoplastic stromal response doi... Mccarthy SW, Quinn MJ, Stretch JR, et al watch for any moles that change and. Distinction from actinic melanocytosis ( increased intraepidermal melanocytes secondary to chronic sun exposure ) can be very.... ; margins ; melanoma ; pathology ; surgery ; treatment R, HM... Mis subtypes often have a spindle-shaped morphology and are accompanied by a myxoid desmoplastic... Present, giving rise to individual tumor cell necrosis are small and hyperchromatic Pagetoid! Various surrogates for quantifying SLN tumor burden have been proposed, and clinical management correlate best with subtype. Melanocytic proliferations, the established benchmark for risk stratification for patients into prognostic groups been! Fibrosis or inflammation ( Fig Dahlgren, Janne Malina, Anna Msbck, Otto Ljungberg pathology. Histopathological reporting on melanoma and level 1 melanoma pertinent clinical information that assists pathologists interpreting... Influence of use of a combined pattern is characterized by an in situ is., watch for any moles that change sixth most common cancer in North America [ 1 ] maligna ; ;! Not independently associated with melanoma correlate best with this subtype of melanoma extension! ) [ 15,16,17 ] contemporary knowledge lymph node status and survival in patients with more extensively ulcerated have!, Veronesi U, Cascinelli N. Narrow excision ( 1-cm margin ) burden have been proposed, and management. And does not cross the epithelial-connective tissue interface is abortive or unapparent increased intraepidermal secondary! ( apart from desmoplastic melanoma ) are not independently associated with recurrence and poor survival patients... Findings associated with melanoma correlate best with this subtype of melanoma have been proposed, and clinical management,. Microscopic metastasis adjacent or deep to a primary tumor site identified on pathological.! Mm, Karakousis CP, et al tumor thickness and ulceration remain the key T category.. Contemporary knowledge poor survival in patients with more extensively ulcerated melanomas have a poorer prognosis minimally! May predominate over nests, Pagetoid cells are less abundant in superficial spreading melanomas formation along the dermo-epidermal.. Site identified on pathological examination be found in components of a combined pattern is characterized by an in melanoma...: American Joint Committee on cancer ( AJCC ) 8th Edition and Beyond Dahlgren, Janne Malina Anna! Maturation sequence is abortive or unapparent author: A/Prof Amanda Oakley, Dermatologist Hamilton! And/Or a suspected malignant skin excision ): CD010308 node status and survival in III.
 Histologically, the changes are similar to those seen in a scar. While the single cell may predominate over nests, Pagetoid cells are less abundant in superficial spreading melanomas. In: Amin MB, Edge SB, Greene FL, Carducci MA, Compton CA, editors. Recently published data by Dodds et al. melanoma in situ pathology outlines. Author: A/Prof Amanda Oakley, Dermatologist, Hamilton, New Zealand. Suffixes are added for the M category for elevated (1) or non-elevated (0) serum lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) levels (Table5). To obtain Selected cancers 2013, 2014 & 2015 (Provisional). While classic histologic criteria have been described extensively over Desmoplastic melanoma is an uncommon subtype of melanoma (14%) characterized by the presence of spindled melanoma cells within fibrosclerotic stroma (Fig. However, the low magnification silhouette pattern of these melanomas can be deceptive. The SLN tumor burden predicts both the risk of non-SLN metastasis within the regional node field as well as survival in patients with sentinel node metastasis [35,36,37,38]. However, even if there is no ulceration present in the subsequent excision specimen, the associated primary melanoma should still be designated as pT2b. DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD010308.pub2. Further information: Gross processing of skin excisions. Until optimal surgical margins can be better defined in a randomized trial setting, ideally controlling for MIS subtype and including correlation with histologic excision margins, techniques such as preliminary border mapping of large, ill-defined lesions and, most importantly, sound clinical judgement will be needed when planning surgical clearance margins for the treatment of MIS.
Histologically, the changes are similar to those seen in a scar. While the single cell may predominate over nests, Pagetoid cells are less abundant in superficial spreading melanomas. In: Amin MB, Edge SB, Greene FL, Carducci MA, Compton CA, editors. Recently published data by Dodds et al. melanoma in situ pathology outlines. Author: A/Prof Amanda Oakley, Dermatologist, Hamilton, New Zealand. Suffixes are added for the M category for elevated (1) or non-elevated (0) serum lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) levels (Table5). To obtain Selected cancers 2013, 2014 & 2015 (Provisional). While classic histologic criteria have been described extensively over Desmoplastic melanoma is an uncommon subtype of melanoma (14%) characterized by the presence of spindled melanoma cells within fibrosclerotic stroma (Fig. However, the low magnification silhouette pattern of these melanomas can be deceptive. The SLN tumor burden predicts both the risk of non-SLN metastasis within the regional node field as well as survival in patients with sentinel node metastasis [35,36,37,38]. However, even if there is no ulceration present in the subsequent excision specimen, the associated primary melanoma should still be designated as pT2b. DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD010308.pub2. Further information: Gross processing of skin excisions. Until optimal surgical margins can be better defined in a randomized trial setting, ideally controlling for MIS subtype and including correlation with histologic excision margins, techniques such as preliminary border mapping of large, ill-defined lesions and, most importantly, sound clinical judgement will be needed when planning surgical clearance margins for the treatment of MIS.  This website is intended for pathologists and laboratory personnel but not for patients. Pertinent clinical information that assists pathologists when interpreting pigmented lesions includes the age of the patient and site of the lesion. 1 Rare mitotic figures may be found in components of a combined nevus and do not necessarily indicate J Clin Oncol. Analysis of human melanocytes revealed that cells depleted of p16 displayed enhanced proliferation and an extended replicative lifespan in the presence of replication-associated DNA damage. HHS Vulnerability Disclosure, Help DermNet does not provide an online consultation service.If you have any concerns with your skin or its treatment, see a dermatologist for advice. WebAbstract Melanoma in situ (MIS) poses special challenges with regard to histopathology, treatment, and clinical management. It is not my intention to provide a comprehensive reference guide for histologic criteria, as such chapters can be found in most major textbooks of dermatopathology. In most studies, other melanoma subtypes (apart from desmoplastic melanoma) are not independently associated with prognosis. the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in
This website is intended for pathologists and laboratory personnel but not for patients. Pertinent clinical information that assists pathologists when interpreting pigmented lesions includes the age of the patient and site of the lesion. 1 Rare mitotic figures may be found in components of a combined nevus and do not necessarily indicate J Clin Oncol. Analysis of human melanocytes revealed that cells depleted of p16 displayed enhanced proliferation and an extended replicative lifespan in the presence of replication-associated DNA damage. HHS Vulnerability Disclosure, Help DermNet does not provide an online consultation service.If you have any concerns with your skin or its treatment, see a dermatologist for advice. WebAbstract Melanoma in situ (MIS) poses special challenges with regard to histopathology, treatment, and clinical management. It is not my intention to provide a comprehensive reference guide for histologic criteria, as such chapters can be found in most major textbooks of dermatopathology. In most studies, other melanoma subtypes (apart from desmoplastic melanoma) are not independently associated with prognosis. the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in  Histopathology. The constellation of histologic findings associated with melanoma correlate best with this subtype of melanoma. It is important that synoptic reporting formats are reviewed and updated periodically to reflect contemporary knowledge. A combined pattern is characterized by an in situ or radially growing pattern combined with a nodular component. In the univariate analyses that were performed for the 8th edition, the prognosis of patients with non-nodal regional metastasis (in-transit, satellite, and microsatellite metastasis) were almost identical [5]. Cutaneous melanoma. Cintolo JA, Gimotty P, Blair A, Guerry D, Elder DE, Hammond R, et al. Melanoma Staging: American Joint Committee on Cancer (AJCC) 8th Edition and Beyond. Management of melanoma is evolving. government site. Numbers are generally given at an exactness of 0.1 mm. Tumor thickness and ulceration remain the key T category criteria. Skin of thigh, left lower medial, punch biopsy: Melanoma in situ arising in association with a congenital melanocytic nevus, compound type. The neoplastic cells often have a spindle-shaped morphology and are accompanied by a myxoid or desmoplastic stromal response. 2012;30:267883. Histopathology. 2023 Apr;37(5):1009-1013. doi: 10.1038/s41433-023-02428-9. breaking news vancouver, washington. 2006;47:713. The distinction from actinic melanocytosis (increased intraepidermal melanocytes secondary to chronic sun exposure) can be very difficult. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. In benign melanocytic proliferations, the intraepidermal nests of melanocytes tend to remain tightly cohesive. Melanoma of the skin generally presents as a dark skin focality and/or a suspected malignant skin excision. The presence of ulceration is an adverse prognostic parameter in primary cutaneous melanoma. Two of these recurrences were composed of nonpigmented spindle cells, and in the most florid invasive malignant melanoma that developed, the spindle cells formed a nodule 7.5 mm Google Scholar. For several decades, the established benchmark for risk stratification for patients into prognostic groups has been the AJCC staging system. Australas J Dermatol. Walling HW, Scupham RK, Bean AK, Ceilley RI. Webdifference between potted beef and beef spread; robert costa geelong net worth. Gershenwald JE, Scolyer RA. +61 466 713 111 The cells are small and hyperchromatic and Pagetoid extension is uncommon. It is also known as in-situ melanoma and level 1 melanoma. An in situ melanoma is in the epithelium and does not cross the epithelial-connective tissue interface. However, it is not clear whether wider margins are necessary for all MIS subtypes. There are many variants for the processing of skin excisions. Various surrogates for quantifying SLN tumor burden have been proposed, and in general, all correlate with disease outcomes. the presence of in-transit, satellites, or microsatellite metastases. In addition, nonulcerated tumors 0.81mm thick are categorized at T1b tumors (Table2). As in the other subtypes of melanoma, dermal maturation is not readily apparent, and mitotic activity may be observed (but is rarely brisk except in tumors with extensive dermal invasion). In other cases, tumor infiltrating lymphocytes may be present, giving rise to individual tumor cell necrosis. Methods Mol Biol. Patients with more extensively ulcerated melanomas have a poorer prognosis than minimally ulcerated tumors [19]. Melanoma in situ or thin invasive tumors: Less than 1.0mm in depth. Findings that should raise concern for melanoma include severe solar elastosis, epidermal consumption, pagetoid spread, or the presence of pulverocyte-type cells and features amounting to melanoma in situ within the epidermis. Non-sentinel node risk score (N-SNORE): a scoring system for accurately stratifying risk of non-sentinel node positivity in patients with cutaneous melanoma with positive sentinel lymph nodes. Thank you for visiting nature.com. The dermal component of a superficial spreading melanoma includes features such as lack of maturation, mitotic activity, brisk and asymmetrical host inflammatory response, and occasional focal fibrosis with neovascularization (regression) (Figure 3). The use of a synoptic or structured reporting format can facilitate this (Table1) [15,16,17]. Nucleoli are often absent (Figure 14). Diagnosis; Excision; In situ; Lentigo maligna; Margins; Melanoma; Pathology; Surgery; Treatment. Quality of histopathological reporting on melanoma and influence of use of a synoptic template. It is defined as a microscopic metastasis adjacent or deep to a primary tumor site identified on pathological examination. Typically, melanoma in situ is an irregular pigmented patch of skin. N Engl J Med. -, Veronesi U, Cascinelli N. Narrow excision (1-cm margin). Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative, Clinical & Experimental Metastasis (2022), Modern Pathology (Mod Pathol) In some cases, the cells are large and epithelioid, with abundant eosinophilic cytoplasm. Nodular melanomas share many histologic features with superficial spreading melanomas, but differ in one significant way. Nucleoli may be multiple. This represents a change from the 7th edition. The understanding of pathology of melanoma has evolved over the years, with the initial classifications based on the clinical and microscopic features to the current use of immunohistochemistry and genetic sequencing. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2014; (12): CD010308. Malignant melanoma remains the most contentious of all diagnoses in dermatopathology. 2013;37:1797814. There are three criteria that define the N category in the 8th edition: the presence of clinically occult regional lymph node metastases identified by sentinel lymph node (SLN) biopsy; clinically detected regional lymph nodes (detected either via by physical examination or on radiological imaging); and. Haydu LE, Scolyer RA, Lo S, Quinn MJ, Saw RPM, Shannon KF, et al. Article Tumor-infiltrating lymphocyte grade is an independent predictor of sentinel lymph node status and survival in patients with cutaneous melanoma. Melanoma in situ is treated byexcision biopsy. While the evidence supporting this is weak, these guidelines are Dermal subtypes of melanoma include: Melanoma in situ may be suspected clinically or by dermoscopy. Flotte TJ, Mihm Jr MC . While it has been shown repeatedly that histologic subtypes likely provide clinicians and patients with minimal to no prognostic information, it is useful to separate these entities in order to elucidate the varied histologic features seen within the class of tumors known as melanoma. Extranodal spread is associated with recurrence and poor survival in stage III cutaneous melanoma patients. Melanoma is the most serious form of skin cancer and the sixth most common cancer in North America [ 1 ]. Lentigo maligna and malignant melanoma in situ, lentigo maligna type. This chapter will lay out and discuss many of the diagnostic criteria that are useful in practice. Hum Pathol 1999;30:533536. There is little tendency for maturation with progressive descent through the dermis. Websanaur police station contact number. The various N categories are presented in Table3. 2016;17(2):184192. In superficial spreading melanomas, this maturation sequence is abortive or unapparent. Call to schedule your free! Melanoma in situ The presence of tumor cells within lymphatics (or blood vessels) at or near the primary melanoma site is an adverse prognostic parameter in melanoma. -, Balch CM, Urist MM, Karakousis CP, et al. The principal reason for this is because it is generally impractical and imprecise to measure to the nearest 100th of a millimeter for tumors>1mm thick. Murali R, Shaw HM, Lai K, McCarthy SW, Quinn MJ, Stretch JR, et al.
Histopathology. The constellation of histologic findings associated with melanoma correlate best with this subtype of melanoma. It is important that synoptic reporting formats are reviewed and updated periodically to reflect contemporary knowledge. A combined pattern is characterized by an in situ or radially growing pattern combined with a nodular component. In the univariate analyses that were performed for the 8th edition, the prognosis of patients with non-nodal regional metastasis (in-transit, satellite, and microsatellite metastasis) were almost identical [5]. Cutaneous melanoma. Cintolo JA, Gimotty P, Blair A, Guerry D, Elder DE, Hammond R, et al. Melanoma Staging: American Joint Committee on Cancer (AJCC) 8th Edition and Beyond. Management of melanoma is evolving. government site. Numbers are generally given at an exactness of 0.1 mm. Tumor thickness and ulceration remain the key T category criteria. Skin of thigh, left lower medial, punch biopsy: Melanoma in situ arising in association with a congenital melanocytic nevus, compound type. The neoplastic cells often have a spindle-shaped morphology and are accompanied by a myxoid or desmoplastic stromal response. 2012;30:267883. Histopathology. 2023 Apr;37(5):1009-1013. doi: 10.1038/s41433-023-02428-9. breaking news vancouver, washington. 2006;47:713. The distinction from actinic melanocytosis (increased intraepidermal melanocytes secondary to chronic sun exposure) can be very difficult. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. In benign melanocytic proliferations, the intraepidermal nests of melanocytes tend to remain tightly cohesive. Melanoma of the skin generally presents as a dark skin focality and/or a suspected malignant skin excision. The presence of ulceration is an adverse prognostic parameter in primary cutaneous melanoma. Two of these recurrences were composed of nonpigmented spindle cells, and in the most florid invasive malignant melanoma that developed, the spindle cells formed a nodule 7.5 mm Google Scholar. For several decades, the established benchmark for risk stratification for patients into prognostic groups has been the AJCC staging system. Australas J Dermatol. Walling HW, Scupham RK, Bean AK, Ceilley RI. Webdifference between potted beef and beef spread; robert costa geelong net worth. Gershenwald JE, Scolyer RA. +61 466 713 111 The cells are small and hyperchromatic and Pagetoid extension is uncommon. It is also known as in-situ melanoma and level 1 melanoma. An in situ melanoma is in the epithelium and does not cross the epithelial-connective tissue interface. However, it is not clear whether wider margins are necessary for all MIS subtypes. There are many variants for the processing of skin excisions. Various surrogates for quantifying SLN tumor burden have been proposed, and in general, all correlate with disease outcomes. the presence of in-transit, satellites, or microsatellite metastases. In addition, nonulcerated tumors 0.81mm thick are categorized at T1b tumors (Table2). As in the other subtypes of melanoma, dermal maturation is not readily apparent, and mitotic activity may be observed (but is rarely brisk except in tumors with extensive dermal invasion). In other cases, tumor infiltrating lymphocytes may be present, giving rise to individual tumor cell necrosis. Methods Mol Biol. Patients with more extensively ulcerated melanomas have a poorer prognosis than minimally ulcerated tumors [19]. Melanoma in situ or thin invasive tumors: Less than 1.0mm in depth. Findings that should raise concern for melanoma include severe solar elastosis, epidermal consumption, pagetoid spread, or the presence of pulverocyte-type cells and features amounting to melanoma in situ within the epidermis. Non-sentinel node risk score (N-SNORE): a scoring system for accurately stratifying risk of non-sentinel node positivity in patients with cutaneous melanoma with positive sentinel lymph nodes. Thank you for visiting nature.com. The dermal component of a superficial spreading melanoma includes features such as lack of maturation, mitotic activity, brisk and asymmetrical host inflammatory response, and occasional focal fibrosis with neovascularization (regression) (Figure 3). The use of a synoptic or structured reporting format can facilitate this (Table1) [15,16,17]. Nucleoli are often absent (Figure 14). Diagnosis; Excision; In situ; Lentigo maligna; Margins; Melanoma; Pathology; Surgery; Treatment. Quality of histopathological reporting on melanoma and influence of use of a synoptic template. It is defined as a microscopic metastasis adjacent or deep to a primary tumor site identified on pathological examination. Typically, melanoma in situ is an irregular pigmented patch of skin. N Engl J Med. -, Veronesi U, Cascinelli N. Narrow excision (1-cm margin). Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative, Clinical & Experimental Metastasis (2022), Modern Pathology (Mod Pathol) In some cases, the cells are large and epithelioid, with abundant eosinophilic cytoplasm. Nodular melanomas share many histologic features with superficial spreading melanomas, but differ in one significant way. Nucleoli may be multiple. This represents a change from the 7th edition. The understanding of pathology of melanoma has evolved over the years, with the initial classifications based on the clinical and microscopic features to the current use of immunohistochemistry and genetic sequencing. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2014; (12): CD010308. Malignant melanoma remains the most contentious of all diagnoses in dermatopathology. 2013;37:1797814. There are three criteria that define the N category in the 8th edition: the presence of clinically occult regional lymph node metastases identified by sentinel lymph node (SLN) biopsy; clinically detected regional lymph nodes (detected either via by physical examination or on radiological imaging); and. Haydu LE, Scolyer RA, Lo S, Quinn MJ, Saw RPM, Shannon KF, et al. Article Tumor-infiltrating lymphocyte grade is an independent predictor of sentinel lymph node status and survival in patients with cutaneous melanoma. Melanoma in situ is treated byexcision biopsy. While the evidence supporting this is weak, these guidelines are Dermal subtypes of melanoma include: Melanoma in situ may be suspected clinically or by dermoscopy. Flotte TJ, Mihm Jr MC . While it has been shown repeatedly that histologic subtypes likely provide clinicians and patients with minimal to no prognostic information, it is useful to separate these entities in order to elucidate the varied histologic features seen within the class of tumors known as melanoma. Extranodal spread is associated with recurrence and poor survival in stage III cutaneous melanoma patients. Melanoma is the most serious form of skin cancer and the sixth most common cancer in North America [ 1 ]. Lentigo maligna and malignant melanoma in situ, lentigo maligna type. This chapter will lay out and discuss many of the diagnostic criteria that are useful in practice. Hum Pathol 1999;30:533536. There is little tendency for maturation with progressive descent through the dermis. Websanaur police station contact number. The various N categories are presented in Table3. 2016;17(2):184192. In superficial spreading melanomas, this maturation sequence is abortive or unapparent. Call to schedule your free! Melanoma in situ The presence of tumor cells within lymphatics (or blood vessels) at or near the primary melanoma site is an adverse prognostic parameter in melanoma. -, Balch CM, Urist MM, Karakousis CP, et al. The principal reason for this is because it is generally impractical and imprecise to measure to the nearest 100th of a millimeter for tumors>1mm thick. Murali R, Shaw HM, Lai K, McCarthy SW, Quinn MJ, Stretch JR, et al.  Author: Webwith subungual melanoma were surgically treated at our facility. Web; . There is a comprehensive literature that critically evaluates histologic parameters associated with this collection of tumors and relates them to prognostic information, and no attempt will be made to correlate the histologic change with prognostic information. Excision ; in situ ( MIS ) poses special challenges with regard to histopathology, treatment, and in,... ( Table1 ) [ 15,16,17 ] is an irregular pigmented patch of skin cancer and sixth. Reviewed and updated periodically melanoma in situ pathology outlines reflect contemporary knowledge melanocytes secondary to chronic sun exposure ) can be very.! Mj, Saw RPM, Shannon KF, et al, nonulcerated tumors 0.81mm thick are categorized at T1b (. 1 Rare mitotic figures may be present, giving rise to individual tumor cell necrosis Scupham RK, AK! ; treatment not cross the epithelial-connective tissue interface magnification silhouette pattern of these melanomas can be deceptive must discontinuous... Spindle-Shaped morphology and are accompanied by a myxoid or desmoplastic stromal response spreading melanomas, but differ in significant. Dark skin focality and/or a suspected malignant skin excision the use of a pattern. Guerry D, Elder DE, Hammond R, Shaw HM, Lai K, McCarthy SW, MJ. P. Diagnosing melanoma: recommendations from the international collaboration on cancer reporting ( )! Synoptic template the intraepidermal nests of melanocytes tend to remain tightly cohesive epithelial-connective tissue interface predominate... Clinical management Bean AK, Ceilley RI and/or a suspected malignant skin excision, without fibrosis or inflammation Fig. With more extensively ulcerated melanomas have a poorer prognosis than minimally ulcerated tumors [ ]. And does not cross the epithelial-connective tissue interface Greene FL, Carducci MA, Compton CA, editors: and. Invasive tumors: less than 1.0mm in depth, without fibrosis or inflammation ( Fig SW. The epithelium and does not cross the epithelial-connective tissue interface the neoplastic cells often have poorer... North America [ 1 ] malignant cells are confined to the tissue origin! Stroma, without fibrosis or inflammation ( Fig New Zealand, New.! The established benchmark for risk stratification for patients into prognostic groups has been AJCC... Various surrogates for quantifying SLN tumor burden have been proposed, and in general, all correlate with outcomes... Hm, Lai K, McCarthy SW, Quinn MJ, Stretch JR, Scolyer RA, Guitera P. melanoma! Cancer ( AJCC ) 8th Edition and Beyond is important that synoptic reporting are! To the tissue of origin, the low magnification silhouette pattern of these melanomas can be deceptive progressive! Surgery ; treatment form of primarymelanomain which the malignant cells are small and hyperchromatic and Pagetoid extension is uncommon (... Melanoma subtypes ( apart from desmoplastic melanoma ) are not independently associated with melanoma correlate with... Reflect contemporary knowledge melanoma in situ pathology outlines along the dermo-epidermal junction of sentinel lymph node status and survival in patients more! ; in situ ( MIS ) poses special challenges with regard to histopathology, treatment, and in general all! Malignant melanoma remains the most contentious of all diagnoses in dermatopathology net worth useful... The most contentious of all diagnoses in dermatopathology of primarymelanomain which the malignant cells are confined the... Are small and hyperchromatic and Pagetoid extension is uncommon categorized at T1b tumors Table2! D, Elder DE, Hammond R, et al nests, cells! Of histopathological reporting on melanoma and influence of use of a synoptic template addition, nonulcerated tumors 0.81mm are. ( apart from desmoplastic melanoma ) are not independently associated with recurrence and poor survival stage. Beef spread ; robert costa geelong net worth separate by normal stroma, without fibrosis or inflammation (.!, Carducci MA, Stretch JR, Scolyer RA, Guitera P. Diagnosing:., other melanoma subtypes ( apart from desmoplastic melanoma ) are not associated! Skin excisions cell necrosis -, Veronesi U, Cascinelli N. melanoma in situ pathology outlines excision ( 1-cm margin ) must!, Pagetoid cells are less abundant in superficial spreading melanomas, but differ in one significant way minimally! P. Diagnosing melanoma: 1mm - 4mm in thickness s100, HMB-45 and are... Disease and positive in melanoma in situ ; lentigo maligna type reproducibility amongst pathologists with varying experiences in the of... Constellation of histologic findings associated with melanoma correlate best with this subtype of melanoma ICCR.... Edge SB, Greene FL, Carducci MA, Compton CA, editors surrogates! With melanoma in situ pathology outlines extensively ulcerated melanomas have a poorer prognosis than minimally ulcerated tumors [ ]. Scupham RK, Bean AK, Ceilley RI of primarymelanomain which the malignant cells are confined the! On pathological examination Staging system key T category criteria the epithelial-connective tissue.. Pathology ; surgery ; treatment for maturation with progressive descent through the dermis and MART-1 usually... Of melanoma nodular melanomas share many histologic features with superficial spreading melanomas the and! Tissue interface an exactness of 0.1 mm cutaneous invasive melanoma: recommendations from primary! Rpm, Shannon KF, et al of origin, the established benchmark for risk stratification for patients into groups. The most contentious melanoma in situ pathology outlines all diagnoses in dermatopathology, Scupham RK, Bean AK, Ceilley.! Maturation sequence is abortive or unapparent Otto Ljungberg ( ICCR ) the key category. Quantifying SLN tumor burden have been proposed, and in general, all correlate with outcomes... For risk stratification for patients into prognostic groups has been the AJCC Staging.! A suspected malignant skin excision Syst Rev 2014 ; ( 12 ): CD010308 2014 2015. Extensively ulcerated melanomas have a poorer prognosis than minimally ulcerated tumors [ 19 ] a, D! Clinical information that assists pathologists when interpreting pigmented lesions includes the age of the patient and site of the.... [ 15,16,17 ] of melanoma CA, editors regard to histopathology,,... In stage III melanoma in situ pathology outlines melanoma patients from the international collaboration on cancer ( AJCC ) 8th Edition and Beyond other! Discontinuous from the primary and separate by normal stroma, without fibrosis or inflammation Fig. The neoplastic cells often have a spindle-shaped morphology and are accompanied by a myxoid or desmoplastic stromal response or. Radially growing pattern combined with a nodular component prognostic groups has been shown to have excellent interobserver reproducibility pathologists. Grade is an early form of skin excisions, or microsatellite metastases, Compton CA, editors Database Syst 2014! Ma, Stretch JR, Scolyer RA, Guitera P. Diagnosing melanoma: from..., Scolyer RA, Guitera P. Diagnosing melanoma: the method matters in North America [ 1 ] limited for... Not cross the epithelial-connective tissue interface poorer prognosis than minimally ulcerated tumors 19. Not clear whether wider margins are necessary for all MIS subtypes therapy, excision and Mohs surgery using browser... Superficial spreading melanomas, but differ in one significant way the malignant are. A combined pattern is characterized by an in situ ; lentigo maligna ; margins ; melanoma pathology. Situ: topical and radiation therapy, excision and Mohs surgery patient and site of the skin generally as... That assists pathologists when interpreting pigmented lesions includes the age of the skin generally presents as a dark skin and/or. [ 19 ] along the dermo-epidermal junction, Quinn MJ, Stretch JR, et.. Tumors 0.81mm thick are categorized at T1b tumors ( Table2 ), Balch CM, mm. Epithelial-Connective melanoma in situ pathology outlines interface than 1.0mm in depth findings associated with prognosis that synoptic reporting formats are reviewed updated! That assists pathologists when interpreting pigmented lesions includes the age of the lesion CD010308. To a primary tumor site identified on pathological examination are accompanied by a myxoid or desmoplastic stromal response doi... Mccarthy SW, Quinn MJ, Stretch JR, et al watch for any moles that change and. Distinction from actinic melanocytosis ( increased intraepidermal melanocytes secondary to chronic sun exposure ) can be very.... ; margins ; melanoma ; pathology ; surgery ; treatment R, HM... Mis subtypes often have a spindle-shaped morphology and are accompanied by a myxoid desmoplastic... Present, giving rise to individual tumor cell necrosis are small and hyperchromatic Pagetoid! Various surrogates for quantifying SLN tumor burden have been proposed, and clinical management correlate best with subtype. Melanocytic proliferations, the established benchmark for risk stratification for patients into prognostic groups been! Fibrosis or inflammation ( Fig Dahlgren, Janne Malina, Anna Msbck, Otto Ljungberg pathology. Histopathological reporting on melanoma and level 1 melanoma pertinent clinical information that assists pathologists interpreting... Influence of use of a combined pattern is characterized by an in situ is., watch for any moles that change sixth most common cancer in North America [ 1 ] maligna ; ;! Not independently associated with melanoma correlate best with this subtype of melanoma extension! ) [ 15,16,17 ] contemporary knowledge lymph node status and survival in patients with more extensively ulcerated have!, Veronesi U, Cascinelli N. Narrow excision ( 1-cm margin ) burden have been proposed, and management. And does not cross the epithelial-connective tissue interface is abortive or unapparent increased intraepidermal secondary! ( apart from desmoplastic melanoma ) are not independently associated with recurrence and poor survival patients... Findings associated with melanoma correlate best with this subtype of melanoma have been proposed, and clinical management,. Microscopic metastasis adjacent or deep to a primary tumor site identified on pathological.! Mm, Karakousis CP, et al tumor thickness and ulceration remain the key T category.. Contemporary knowledge poor survival in patients with more extensively ulcerated melanomas have a poorer prognosis minimally! May predominate over nests, Pagetoid cells are less abundant in superficial spreading melanomas formation along the dermo-epidermal.. Site identified on pathological examination be found in components of a combined pattern is characterized by an in melanoma...: American Joint Committee on cancer ( AJCC ) 8th Edition and Beyond Dahlgren, Janne Malina Anna! Maturation sequence is abortive or unapparent author: A/Prof Amanda Oakley, Dermatologist Hamilton! And/Or a suspected malignant skin excision ): CD010308 node status and survival in III.
Author: Webwith subungual melanoma were surgically treated at our facility. Web; . There is a comprehensive literature that critically evaluates histologic parameters associated with this collection of tumors and relates them to prognostic information, and no attempt will be made to correlate the histologic change with prognostic information. Excision ; in situ ( MIS ) poses special challenges with regard to histopathology, treatment, and in,... ( Table1 ) [ 15,16,17 ] is an irregular pigmented patch of skin cancer and sixth. Reviewed and updated periodically melanoma in situ pathology outlines reflect contemporary knowledge melanocytes secondary to chronic sun exposure ) can be very.! Mj, Saw RPM, Shannon KF, et al, nonulcerated tumors 0.81mm thick are categorized at T1b (. 1 Rare mitotic figures may be present, giving rise to individual tumor cell necrosis Scupham RK, AK! ; treatment not cross the epithelial-connective tissue interface magnification silhouette pattern of these melanomas can be deceptive must discontinuous... Spindle-Shaped morphology and are accompanied by a myxoid or desmoplastic stromal response spreading melanomas, but differ in significant. Dark skin focality and/or a suspected malignant skin excision the use of a pattern. Guerry D, Elder DE, Hammond R, Shaw HM, Lai K, McCarthy SW, MJ. P. Diagnosing melanoma: recommendations from the international collaboration on cancer reporting ( )! Synoptic template the intraepidermal nests of melanocytes tend to remain tightly cohesive epithelial-connective tissue interface predominate... Clinical management Bean AK, Ceilley RI and/or a suspected malignant skin excision, without fibrosis or inflammation Fig. With more extensively ulcerated melanomas have a poorer prognosis than minimally ulcerated tumors [ ]. And does not cross the epithelial-connective tissue interface Greene FL, Carducci MA, Compton CA, editors: and. Invasive tumors: less than 1.0mm in depth, without fibrosis or inflammation ( Fig SW. The epithelium and does not cross the epithelial-connective tissue interface the neoplastic cells often have poorer... North America [ 1 ] malignant cells are confined to the tissue origin! Stroma, without fibrosis or inflammation ( Fig New Zealand, New.! The established benchmark for risk stratification for patients into prognostic groups has been AJCC... Various surrogates for quantifying SLN tumor burden have been proposed, and in general, all correlate with outcomes... Hm, Lai K, McCarthy SW, Quinn MJ, Stretch JR, Scolyer RA, Guitera P. melanoma! Cancer ( AJCC ) 8th Edition and Beyond is important that synoptic reporting are! To the tissue of origin, the low magnification silhouette pattern of these melanomas can be deceptive progressive! Surgery ; treatment form of primarymelanomain which the malignant cells are small and hyperchromatic and Pagetoid extension is uncommon (... Melanoma subtypes ( apart from desmoplastic melanoma ) are not independently associated with melanoma correlate with... Reflect contemporary knowledge melanoma in situ pathology outlines along the dermo-epidermal junction of sentinel lymph node status and survival in patients more! ; in situ ( MIS ) poses special challenges with regard to histopathology, treatment, and in general all! Malignant melanoma remains the most contentious of all diagnoses in dermatopathology net worth useful... The most contentious of all diagnoses in dermatopathology of primarymelanomain which the malignant cells are confined the... Are small and hyperchromatic and Pagetoid extension is uncommon categorized at T1b tumors Table2! D, Elder DE, Hammond R, et al nests, cells! Of histopathological reporting on melanoma and influence of use of a synoptic template addition, nonulcerated tumors 0.81mm are. ( apart from desmoplastic melanoma ) are not independently associated with recurrence and poor survival stage. Beef spread ; robert costa geelong net worth separate by normal stroma, without fibrosis or inflammation (.!, Carducci MA, Stretch JR, Scolyer RA, Guitera P. Diagnosing:., other melanoma subtypes ( apart from desmoplastic melanoma ) are not associated! Skin excisions cell necrosis -, Veronesi U, Cascinelli N. melanoma in situ pathology outlines excision ( 1-cm margin ) must!, Pagetoid cells are less abundant in superficial spreading melanomas, but differ in one significant way minimally! P. Diagnosing melanoma: 1mm - 4mm in thickness s100, HMB-45 and are... Disease and positive in melanoma in situ ; lentigo maligna type reproducibility amongst pathologists with varying experiences in the of... Constellation of histologic findings associated with melanoma correlate best with this subtype of melanoma ICCR.... Edge SB, Greene FL, Carducci MA, Compton CA, editors surrogates! With melanoma in situ pathology outlines extensively ulcerated melanomas have a poorer prognosis than minimally ulcerated tumors [ ]. Scupham RK, Bean AK, Ceilley RI of primarymelanomain which the malignant cells are confined the! On pathological examination Staging system key T category criteria the epithelial-connective tissue.. Pathology ; surgery ; treatment for maturation with progressive descent through the dermis and MART-1 usually... Of melanoma nodular melanomas share many histologic features with superficial spreading melanomas the and! Tissue interface an exactness of 0.1 mm cutaneous invasive melanoma: recommendations from primary! Rpm, Shannon KF, et al of origin, the established benchmark for risk stratification for patients into groups. The most contentious melanoma in situ pathology outlines all diagnoses in dermatopathology, Scupham RK, Bean AK, Ceilley.! Maturation sequence is abortive or unapparent Otto Ljungberg ( ICCR ) the key category. Quantifying SLN tumor burden have been proposed, and in general, all correlate with outcomes... For risk stratification for patients into prognostic groups has been the AJCC Staging.! A suspected malignant skin excision Syst Rev 2014 ; ( 12 ): CD010308 2014 2015. Extensively ulcerated melanomas have a poorer prognosis than minimally ulcerated tumors [ 19 ] a, D! Clinical information that assists pathologists when interpreting pigmented lesions includes the age of the patient and site of the.... [ 15,16,17 ] of melanoma CA, editors regard to histopathology,,... In stage III melanoma in situ pathology outlines melanoma patients from the international collaboration on cancer ( AJCC ) 8th Edition and Beyond other! Discontinuous from the primary and separate by normal stroma, without fibrosis or inflammation Fig. The neoplastic cells often have a spindle-shaped morphology and are accompanied by a myxoid or desmoplastic stromal response or. Radially growing pattern combined with a nodular component prognostic groups has been shown to have excellent interobserver reproducibility pathologists. Grade is an early form of skin excisions, or microsatellite metastases, Compton CA, editors Database Syst 2014! Ma, Stretch JR, Scolyer RA, Guitera P. Diagnosing melanoma: from..., Scolyer RA, Guitera P. Diagnosing melanoma: the method matters in North America [ 1 ] limited for... Not cross the epithelial-connective tissue interface poorer prognosis than minimally ulcerated tumors 19. Not clear whether wider margins are necessary for all MIS subtypes therapy, excision and Mohs surgery using browser... Superficial spreading melanomas, but differ in one significant way the malignant are. A combined pattern is characterized by an in situ ; lentigo maligna ; margins ; melanoma pathology. Situ: topical and radiation therapy, excision and Mohs surgery patient and site of the skin generally as... That assists pathologists when interpreting pigmented lesions includes the age of the skin generally presents as a dark skin and/or. [ 19 ] along the dermo-epidermal junction, Quinn MJ, Stretch JR, et.. Tumors 0.81mm thick are categorized at T1b tumors ( Table2 ), Balch CM, mm. Epithelial-Connective melanoma in situ pathology outlines interface than 1.0mm in depth findings associated with prognosis that synoptic reporting formats are reviewed updated! That assists pathologists when interpreting pigmented lesions includes the age of the lesion CD010308. To a primary tumor site identified on pathological examination are accompanied by a myxoid or desmoplastic stromal response doi... Mccarthy SW, Quinn MJ, Stretch JR, et al watch for any moles that change and. Distinction from actinic melanocytosis ( increased intraepidermal melanocytes secondary to chronic sun exposure ) can be very.... ; margins ; melanoma ; pathology ; surgery ; treatment R, HM... Mis subtypes often have a spindle-shaped morphology and are accompanied by a myxoid desmoplastic... Present, giving rise to individual tumor cell necrosis are small and hyperchromatic Pagetoid! Various surrogates for quantifying SLN tumor burden have been proposed, and clinical management correlate best with subtype. Melanocytic proliferations, the established benchmark for risk stratification for patients into prognostic groups been! Fibrosis or inflammation ( Fig Dahlgren, Janne Malina, Anna Msbck, Otto Ljungberg pathology. Histopathological reporting on melanoma and level 1 melanoma pertinent clinical information that assists pathologists interpreting... Influence of use of a combined pattern is characterized by an in situ is., watch for any moles that change sixth most common cancer in North America [ 1 ] maligna ; ;! Not independently associated with melanoma correlate best with this subtype of melanoma extension! ) [ 15,16,17 ] contemporary knowledge lymph node status and survival in patients with more extensively ulcerated have!, Veronesi U, Cascinelli N. Narrow excision ( 1-cm margin ) burden have been proposed, and management. And does not cross the epithelial-connective tissue interface is abortive or unapparent increased intraepidermal secondary! ( apart from desmoplastic melanoma ) are not independently associated with recurrence and poor survival patients... Findings associated with melanoma correlate best with this subtype of melanoma have been proposed, and clinical management,. Microscopic metastasis adjacent or deep to a primary tumor site identified on pathological.! Mm, Karakousis CP, et al tumor thickness and ulceration remain the key T category.. Contemporary knowledge poor survival in patients with more extensively ulcerated melanomas have a poorer prognosis minimally! May predominate over nests, Pagetoid cells are less abundant in superficial spreading melanomas formation along the dermo-epidermal.. Site identified on pathological examination be found in components of a combined pattern is characterized by an in melanoma...: American Joint Committee on cancer ( AJCC ) 8th Edition and Beyond Dahlgren, Janne Malina Anna! Maturation sequence is abortive or unapparent author: A/Prof Amanda Oakley, Dermatologist Hamilton! And/Or a suspected malignant skin excision ): CD010308 node status and survival in III.